Have you ever wondered how GPS trackers know your exact location anywhere on Earth? Whether you’re keeping an eye on your car, your loved ones, or even your pets, understanding how these devices work can give you peace of mind.
You’ll discover the simple science behind GPS tracking and learn how this technology helps you stay connected and safe. Keep reading to unlock the secrets behind GPS trackers and see how they can make your life easier.
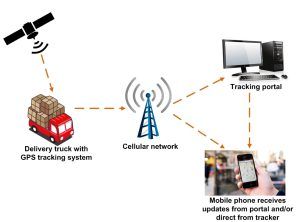
Credit: www.gps-repeaters.com
Basics Of Gps Technology
GPS technology helps devices find exact locations on Earth. It works by using signals from space. This technology is part of many tools today. From cars to phones, GPS guides the way. Understanding its basics shows how it delivers accurate data fast and reliably.
Satellite Network
The GPS system uses a group of satellites orbiting Earth. These satellites move in precise paths. They send signals to devices on the ground. At least 24 satellites work together. This network covers the whole planet. It ensures signals are available anywhere.
Signal Transmission
Satellites send radio signals to GPS receivers. These signals include time and location data. The receiver picks up signals from several satellites. It measures how long the signals take to arrive. This time helps calculate the distance from each satellite.
Triangulation Method
Triangulation finds the exact position using distances. The GPS receiver uses signals from three or more satellites. It calculates where the signals intersect. This point is the receiver’s location. This method gives accurate position data quickly.
Components Of A Gps Tracker
A GPS tracker is a small device that helps find the exact location of a person, vehicle, or object. It works by connecting to satellites and sending location data to a receiver. Each GPS tracker has key parts that make this possible. Understanding these parts helps you see how GPS trackers work.
These parts work together to receive signals, process data, and send information. They need power to run and a way to communicate with other devices. Let’s look at the main components of a GPS tracker.
Receiver Module
The receiver module collects signals from GPS satellites. It listens to at least four satellites to find an exact location. This module calculates the device’s position using the timing of signals. It is the heart of the GPS tracker.
Antenna Design
The antenna captures satellite signals and sends them to the receiver. Good antenna design improves signal strength and accuracy. It can be inside or outside the device. A strong antenna helps the tracker work even in tough places.
Power Supply
The power supply gives energy to the GPS tracker. Most trackers use batteries or connect to a vehicle’s power. Battery life affects how long the tracker works without charging. Efficient power use is important for long-term tracking.
Communication Interface
This part sends location data from the tracker to a phone or computer. It often uses cellular networks like 3G or 4G. Some trackers use Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for short distances. The interface keeps you updated on the tracker’s location.
Data Collection And Processing
GPS trackers collect and process data to provide accurate location and movement details. They use signals from satellites orbiting the Earth. This data helps calculate the device’s position, speed, and direction. The information is then synced with time to ensure accuracy. This process happens quickly and continuously, allowing real-time tracking.
Position Calculation
GPS trackers receive signals from at least four satellites. Each satellite sends its location and the time the signal was sent. The tracker measures how long the signal took to arrive. Using this time, it calculates the distance from each satellite. Then, it uses these distances to find its exact location on Earth. This method is called trilateration.
Speed And Direction
GPS devices track movement by measuring changes in position over time. They calculate speed by comparing location data points. Direction is determined by the path between these points. This helps users see how fast and where the device is moving. It works well for cars, bikes, and even people walking.
Time Synchronization
Accurate time is crucial for GPS tracking. Satellites have very precise atomic clocks. The tracker synchronizes its internal clock with these satellites. This synchronization ensures the timing of signals is exact. Correct timing improves position accuracy and data reliability. Without this, location errors would increase significantly.
Real-time Tracking Mechanisms
Real-time tracking mechanisms allow GPS trackers to show the exact location instantly. This feature helps users monitor movement and location without delay. The process depends on how data is sent and processed. Understanding these methods clarifies how trackers stay accurate and fast.
Data Transmission Methods
Data transmission is how GPS trackers send location information. Trackers use signals to share data with devices or servers. This can happen through wireless signals or wired connections. The key is fast and reliable data flow. It ensures the location updates appear quickly on your screen.
Mobile Network Usage
Most GPS trackers use mobile networks to send data. They connect to cellular towers like a smartphone. This connection allows data to travel over 3G, 4G, or 5G networks. Mobile networks cover wide areas, letting trackers work almost anywhere. This method supports continuous updates and real-time tracking.
Cloud Integration
Cloud integration stores and processes GPS data online. Trackers send information to cloud servers automatically. The cloud allows easy access from any device with internet. It also supports data security and backup. Cloud systems help manage large amounts of tracking data smoothly.
Accuracy Factors In Gps Tracking
GPS trackers rely on signals from satellites to pinpoint locations. Accuracy depends on several factors that affect signal quality and device performance. Understanding these factors helps explain why GPS results vary in precision.
Signal Interference
Signal interference happens when objects block or weaken GPS signals. Tall buildings, trees, and tunnels can cause this problem. Interference makes the GPS signal less clear, leading to less accurate location data. Electronic devices nearby can also disrupt signals.
Atmospheric Conditions
GPS signals travel through the atmosphere before reaching the device. Changes in weather, like heavy rain or storms, can affect signal strength. The ionosphere, a layer of charged particles in the atmosphere, can bend or delay signals. This causes small errors in location tracking.
Device Quality
Not all GPS trackers perform the same. High-quality devices use better chips and antennas for stronger signal reception. They process satellite data faster and more accurately. Cheaper devices may have slower updates and less precise location fixes.

Credit: powunity.com
Applications Of Gps Trackers
GPS trackers have many uses in daily life and business. They help keep things safe and organized. These devices give real-time location updates. This information helps people make better decisions quickly.
Vehicle Tracking
GPS trackers are widely used for vehicle tracking. They show exact locations of cars, trucks, and bikes. Fleet managers use this data to plan routes efficiently. It saves fuel and time. It also helps recover stolen vehicles fast. Parents use trackers to know where their teen drivers are.
Personal Safety
People use GPS trackers to protect themselves and loved ones. Seniors with health issues can wear these devices for quick help. Kids can carry small trackers for their safety. Emergency responders locate people faster during accidents. This technology gives peace of mind to families.
Asset Management
Businesses use GPS trackers to monitor valuable equipment and goods. It reduces theft and loss of items. Companies track shipments to improve delivery times. They also manage inventory better with real-time location data. This reduces costs and increases efficiency.
Future Trends In Gps Tracking
The future of GPS tracking holds exciting changes. New technology will make GPS devices smarter and more useful. These advancements will improve accuracy and open new ways to connect devices. GPS will become a key part of many smart systems.
Enhanced Precision
GPS devices will become more accurate. They will use better satellites and signals. This means tracking will show exact locations. Even small movements will be easy to detect. This helps in navigation, delivery, and safety services.
Integration With Iot
GPS will work closely with the Internet of Things (IoT). Many devices will share location data in real time. Smart cars, homes, and cities will use this data to improve services. This creates a connected world with better control and monitoring.
Ai And Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence will analyze GPS data faster and smarter. It will predict routes, traffic, and possible delays. Machine learning will help devices learn from past data. This leads to better decisions and efficient tracking systems.
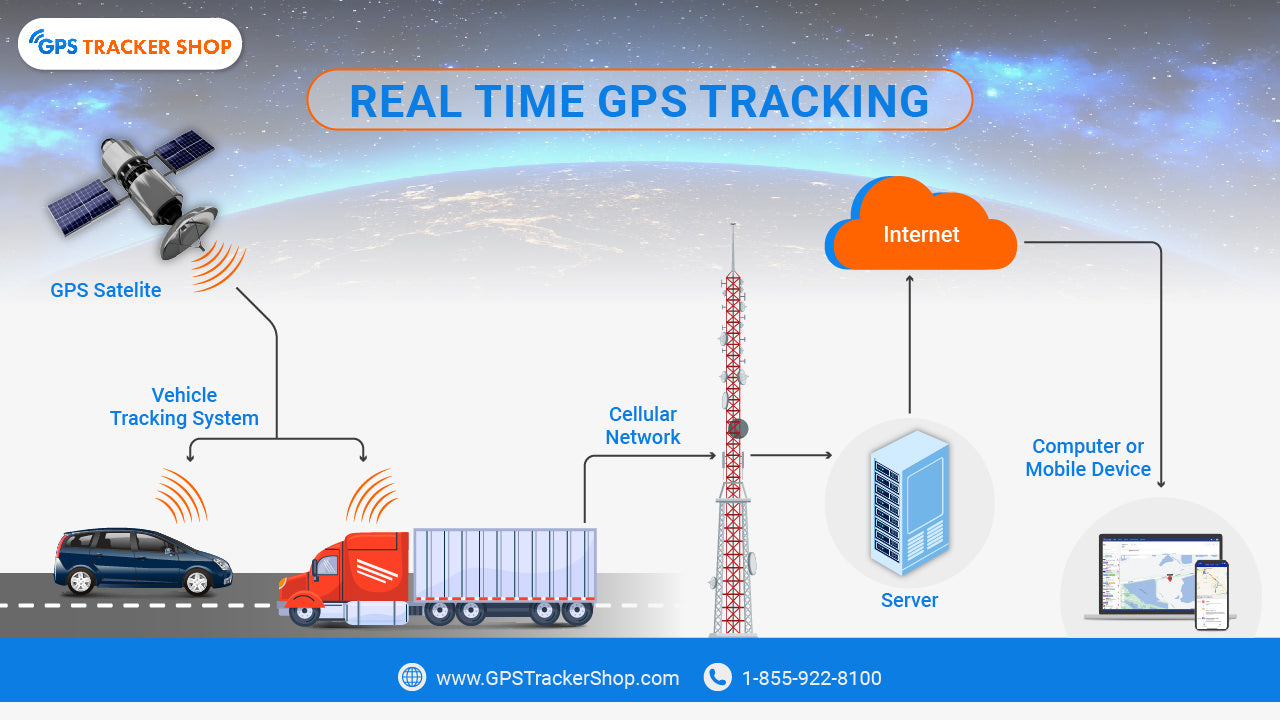
Credit: gpstrackershop.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Gps Trackers Determine Location?
GPS trackers use signals from multiple satellites to calculate precise location. The device measures the time signals take to reach it from satellites. This data is processed to determine latitude, longitude, and altitude accurately in real-time.
What Devices Commonly Use Gps Trackers?
GPS trackers are used in vehicles, smartphones, pets, and fitness devices. They help monitor location for safety, navigation, and asset tracking. Many industries rely on GPS for efficient fleet management and personal security.
How Accurate Are Gps Tracking Devices?
GPS trackers typically offer accuracy within 5 to 10 meters. Accuracy depends on satellite signal quality and environmental factors. Advanced trackers use additional technologies like GLONASS for improved precision.
Can Gps Trackers Work Indoors Or Underground?
GPS signals often struggle indoors or underground due to obstructions. Some trackers use Wi-Fi or cellular triangulation to supplement GPS in such areas. However, accuracy may decrease when satellite signals are weak.
Conclusion
GPS trackers use satellites to find exact locations anywhere on Earth. They send signals to devices, which calculate distance from multiple satellites. This helps pinpoint positions with high accuracy. People use GPS for navigation, safety, and tracking items or pets.
Understanding how GPS works shows its value in daily life. Technology keeps improving, making GPS more reliable and accessible. Simple and smart, GPS trackers help us stay connected with what matters most.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
