Are you wondering how to calculate your attrition rate but don’t know where to start? Understanding this number is crucial for keeping your business healthy and your team strong.
Knowing your attrition rate helps you spot problems early and make smarter decisions about hiring and retention. You’ll learn a simple, step-by-step method to calculate your attrition rate accurately. By the end, you’ll have the tools to track this key metric with confidence—and use it to improve your workplace.
Let’s dive in and make attrition rate work for you.
What Is Attrition Rate
Attrition rate shows how many people leave a group over time. To calculate it, divide the number who left by the total number at the start, then multiply by 100. This gives a clear percentage of turnover.
Attrition rate shows how many people leave a group over time. It helps companies understand staff turnover or customer loss. Knowing this rate guides decisions to improve retention.
Attrition rate measures the percentage of people who exit during a specific period. It can apply to employees, customers, or students. This rate highlights patterns that need attention.
High attrition rate can signal problems in the workplace or service quality. It affects costs, productivity, and team morale. Tracking attrition helps identify issues early and reduce losses.
Types Of Attrition Rate
Employee attrition rate counts workers leaving a company. Customer attrition rate tracks clients who stop buying or using services. Student attrition rate measures learners who drop out of courses.
Credit: www.educba.com
Why Attrition Rate Matters
Attrition rate shows how many people leave a group over time. It helps businesses understand their workforce stability. High attrition can signal problems in the workplace. Low attrition often means employees are satisfied and loyal.
Tracking attrition helps managers make better decisions. It points out areas needing improvement. It also helps forecast future hiring needs. Knowing attrition rate supports planning and budgeting.
Impact On Company Growth
A high attrition rate can slow down growth. Losing skilled employees means losing knowledge. New hires take time to train and adjust. This can delay projects and reduce output.
Stable teams work faster and produce better results. Keeping attrition low helps maintain steady progress. Companies with low attrition grow more smoothly.
Cost Of Employee Turnover
Replacing workers costs money. Expenses include recruiting, training, and lost productivity. High attrition increases these costs significantly. This can hurt a company’s budget and profits.
Lower attrition means fewer hiring costs. It saves money and resources. Understanding attrition helps control these expenses.
Effect On Workplace Morale
Frequent employee departures can harm morale. Remaining workers may feel stressed or worried. This leads to lower motivation and performance.
Good retention creates a positive work environment. Employees feel secure and valued. This boosts teamwork and productivity.
Insight Into Employee Satisfaction
Attrition rate reflects how happy employees are. High rates often indicate dissatisfaction or issues. Low rates suggest good management and culture.
Tracking this metric helps identify problems early. Employers can then take steps to improve conditions. This keeps staff engaged and loyal.
Key Terms To Know
Understanding key terms helps you calculate attrition rate correctly. These terms explain what numbers to use and what they mean. Knowing these words makes the process clearer and easier.
Attrition Rate
Attrition rate shows how many employees leave a company over time. It is usually shown as a percentage. This rate helps businesses see how stable their workforce is.
Employee Turnover
Employee turnover means the number of workers who leave and get replaced. It is different from attrition because turnover includes hiring new staff. Turnover measures how often staff changes happen.
Starting Headcount
Starting headcount is the number of employees at the beginning of a period. This number is needed to find the attrition rate. It sets the base for comparison.
Ending Headcount
Ending headcount counts employees at the end of a period. It shows how many staff remain after some leave. This helps understand workforce changes.
Voluntary Attrition
Voluntary attrition means employees leave by their own choice. These are resignations or retirements. Tracking this helps find reasons why staff leave.
Involuntary Attrition
Involuntary attrition happens when employees are let go. This includes layoffs or firings. It shows parts of attrition not caused by employee choice.
.webp)
Credit: www.learnerbly.com
Basic Formula For Attrition Rate
Understanding the basic formula for attrition rate helps track employee turnover. This metric shows how many workers leave a company over a period. Calculating it is simple and gives clear insights.
Knowing the attrition rate helps businesses manage staff better. It also guides decisions to improve work conditions and retain employees.
What Is Attrition Rate?
Attrition rate measures the percentage of employees leaving a company. It usually covers a set time, like a month or a year. This rate helps see if turnover is low or high.
Basic Formula Explained
The formula for attrition rate is easy to use. Take the number of employees who left during a period. Divide that by the total number of employees at the start. Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage.
Formula Example
Imagine 10 employees leave in a year. The company started the year with 200 staff. Divide 10 by 200, which equals 0.05. Multiply by 100 to get 5%. The attrition rate is 5% for that year.
Step-by-step Calculation Guide
Calculating the attrition rate helps track employee turnover in a company. It shows how many employees leave over a period. This guide breaks down the process into simple steps. Follow these steps to get clear, useful results.
Gathering Employee Data
Start by collecting employee records. Note how many employees started and ended the period. Include full-time, part-time, and contract workers if needed. Use accurate, up-to-date data for best results.
Determining Time Period
Choose the time frame for your calculation. Common periods include monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Match the period with your business needs. Consistency helps track trends over time.
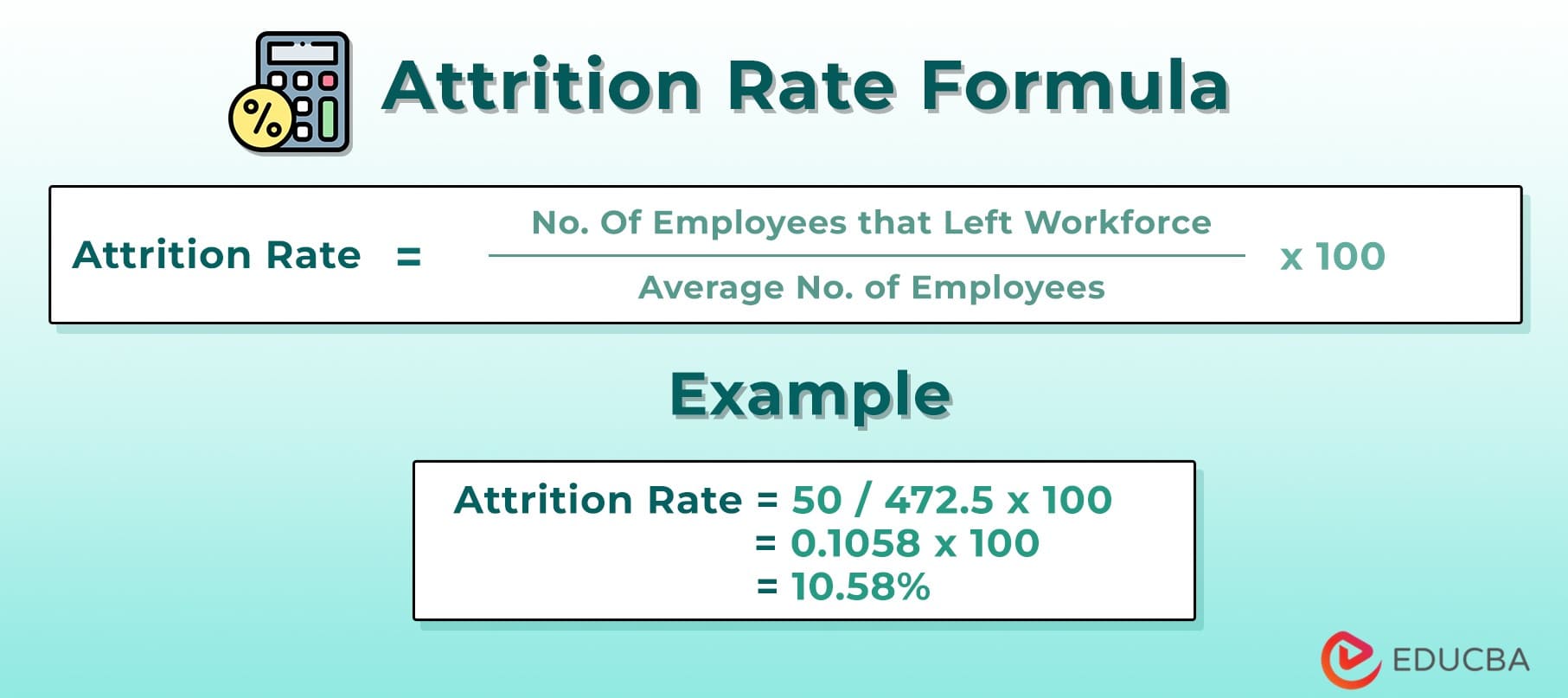
Applying The Formula
The basic formula is: (Number of employees who left ÷ Average number of employees) × 100. Calculate the average by adding the number at the start and end, then divide by two. Plug in the numbers and solve.
Interpreting Results
Look at the percentage to understand turnover. A low rate means good employee retention. A high rate may indicate problems. Compare results with industry standards to see where you stand.
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Calculating the attrition rate seems simple, but many make common errors. These mistakes can lead to wrong numbers and poor decisions. Avoiding these errors helps keep your data clear and useful.
Incorrect Time Period Selection
Choosing the wrong time frame affects attrition rate accuracy. Use consistent periods like monthly, quarterly, or yearly. Mixing different time frames causes confusion and wrong results.
Ignoring Employee Types
Counting all employees without distinction can skew results. Separate full-time, part-time, and temporary workers. Each group has different turnover patterns to consider.
Not Accounting For New Hires
Forgetting new hires in the calculation lowers the attrition rate. Always include the average number of employees, factoring in new staff. This gives a balanced view of workforce changes.
Mixing Voluntary And Involuntary Turnover
Combining voluntary resignations with layoffs or retirements hides true attrition reasons. Track these separately to understand why employees leave. This helps target specific problems.
Using Headcount Instead Of Full-time Equivalents
Counting people without adjusting for work hours distorts the rate. Use full-time equivalents (FTE) to standardize employee numbers. This method reflects real workforce size better.
Using Attrition Rate For Business Decisions
Using attrition rate helps businesses understand employee turnover clearly. It shows how many workers leave a company over time. This data guides important decisions that improve workplace stability and growth.
Attrition rate reveals patterns. It points out departments with high turnover. Managers use this info to fix problems and keep good employees longer.
Identifying Workforce Trends
Attrition rate helps spot trends in staff changes. It shows which teams lose more workers. Businesses watch these trends to plan hiring and training better.
Improving Employee Retention
Knowing the attrition rate highlights retention issues. Companies can create policies to keep workers happy. This lowers turnover and saves hiring costs.
Budget Planning And Cost Control
High attrition means more recruitment costs. Understanding this helps plan budgets wisely. Businesses allocate funds to hiring and employee development smartly.
Enhancing Recruitment Strategies
Attrition data informs recruitment efforts. It shows the types of employees who stay longer. Hiring teams focus on finding candidates who fit well.
Measuring Impact Of Changes
After changes in work culture or policies, attrition rate shows results. Businesses check if turnover drops or rises. This measure guides future improvements.

Credit: www.continu.com
Tools And Software Recommendations
Calculating attrition rate becomes easier with the right tools and software. These solutions help track employee numbers and turnover automatically. They reduce errors and save time. Many options suit different business sizes and needs.
Hr Management Systems
HR management systems often include attrition tracking features. They store employee data and generate reports quickly. Systems like BambooHR and Zoho People provide clear dashboards. Managers can see trends and act fast.
Spreadsheet Software
Spreadsheets like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets offer flexible calculation options. You can build simple attrition rate formulas. They work well for small teams or startups. Templates are available to make the process smooth.
Employee Analytics Platforms
Employee analytics platforms focus on workforce data and insights. Tools such as Visier and PeopleInsight analyze turnover causes. They help identify patterns behind attrition. This aids in better decision-making and planning.
Payroll Software
Payroll software can track employee exits linked to salary data. Products like Gusto and ADP offer basic attrition reports. These tools simplify tracking workforce changes alongside payments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Attrition Rate In Simple Terms?
Attrition rate measures employee turnover in a company over time. It shows the percentage of staff leaving voluntarily or involuntarily during a period. It helps assess workforce stability and retention challenges.
How Do I Calculate Attrition Rate Formula?
Divide the number of employees who left by the average total employees, then multiply by 100. This gives the attrition rate percentage for the period.
Why Is Calculating Attrition Rate Important?
Calculating attrition helps identify hiring needs, reduce turnover costs, and improve employee satisfaction. It guides HR strategies and business planning effectively.
What Time Period Should I Use To Calculate Attrition?
Commonly, attrition is calculated monthly, quarterly, or annually. Choose a period that aligns with your business reporting and HR goals for accurate insights.
Conclusion
Calculating attrition rate helps you understand employee turnover clearly. This number shows how many leave your company in a time period. Keep tracking it regularly to see patterns or changes. Knowing this rate guides you to improve work conditions and keep good staff.
It also helps in planning for future hiring needs. Use simple formulas and accurate data for best results. Remember, a clear attrition rate supports better business decisions and growth.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

