Have you ever wondered what happens inside your digital camera every time you snap a photo? Understanding how a digital camera works can change the way you capture memories and help you take better pictures.
Imagine knowing exactly what makes your camera tick, so you can use it smarter and get stunning shots every time. You’ll discover the simple steps your camera follows to turn a moment into a perfect image. Ready to unlock the secret behind your camera’s magic?
Keep reading—you’ll be surprised how easy it is!

Credit: www.youtube.com
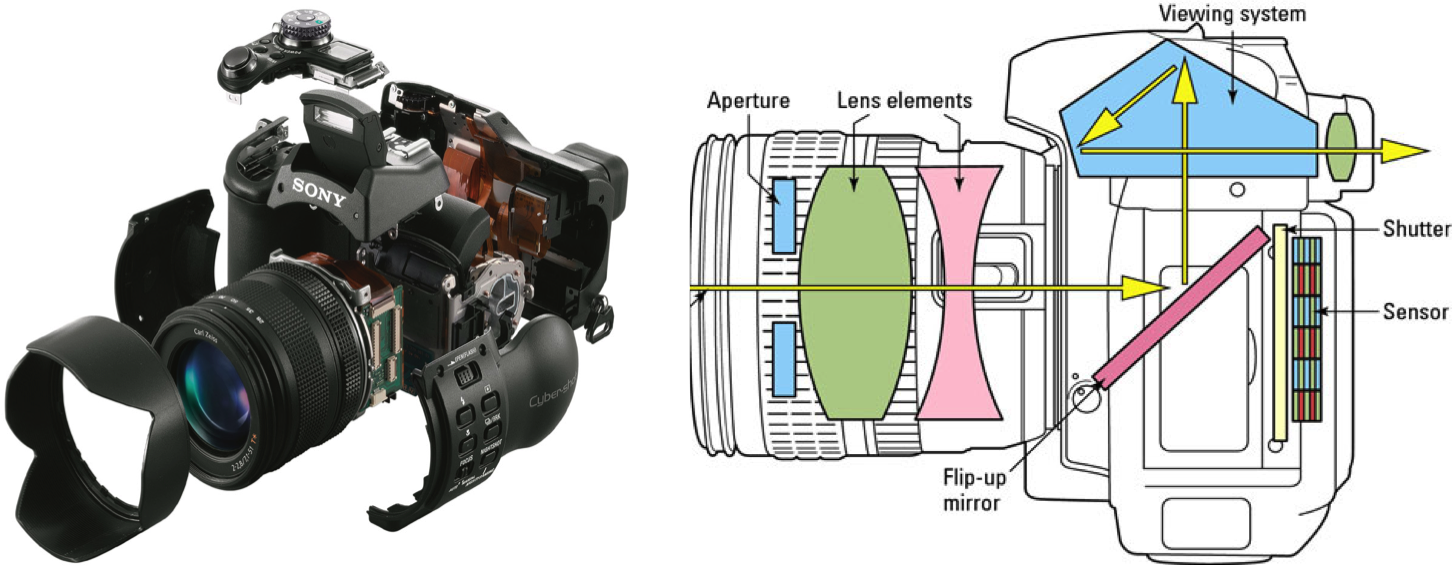
Camera Components
Cameras are made of several important parts. Each part has a special job. These parts work together to take clear and sharp photos. Understanding these parts helps you see how a digital camera works.
Lens And Aperture
The lens focuses light onto the camera’s sensor. It controls how much light enters through the aperture. The aperture is like a small window that opens and closes. A bigger opening lets in more light. A smaller opening lets in less light. This helps adjust the brightness and depth of field in photos.
Image Sensor
The image sensor captures the light from the lens. It changes light into electrical signals. These signals form the digital image. Sensors come in different sizes and types. Larger sensors usually produce better image quality. The sensor’s role is very important for clear photos.
Shutter Mechanism
The shutter controls the time the sensor is exposed to light. It opens and closes quickly to capture the image. The speed of the shutter affects motion blur. A fast shutter freezes movement. A slow shutter can create motion effects. This part helps manage exposure and sharpness.
Processor And Memory
The processor handles the image data from the sensor. It processes and improves the photo quality. The processor also controls camera functions and settings. The memory stores the final photos. Memory cards save pictures for later use. This system works fast to keep up with shooting.
Capturing Light
Capturing light is the heart of how a digital camera works. Without light, a camera cannot create an image. The process begins when light enters the camera lens and ends with a digital image stored in memory. Understanding this process helps you take better photos and control your camera settings.
Light Entry And Focus
Light enters the camera through the lens. The lens gathers light from the scene and directs it to the camera’s sensor. The sensor is like the camera’s eye, catching the light to form a picture. Focus adjusts the lens to make the image sharp and clear. If the focus is wrong, the picture looks blurry.
Role Of The Aperture
The aperture controls how much light enters the camera. It is a small hole inside the lens that can open wide or close down. A wide aperture lets in more light, good for dark scenes. A small aperture lets less light in, useful in bright conditions. Aperture also affects how much of the image is in focus.
Shutter Speed Impact
Shutter speed controls how long light hits the sensor. A fast shutter speed captures quick action without blur. A slow shutter speed lets in more light but can cause motion blur. Choosing the right shutter speed balances light and movement in your photo.
Image Sensor Function
The image sensor is the heart of a digital camera. It captures light and turns it into a digital picture. This process is key to creating clear and colorful images. Understanding how the image sensor works helps explain how cameras capture moments so well.
The sensor sits behind the camera lens. It receives the light that passes through the lens and changes it into electrical signals. These signals form the base of every photo you take.
Converting Light To Electrical Signals
The image sensor collects light from the scene. It uses tiny parts that react to light called photodiodes. Each photodiode measures how much light hits it. The sensor then changes this light into electrical signals.
The strength of the electrical signal shows the light’s brightness. Stronger light makes a stronger signal. The camera’s processor reads these signals to build the image.
Pixel Structure
Pixels are small squares on the image sensor. Each pixel captures light from a tiny part of the scene. Many pixels work together to form a full picture. More pixels mean better detail in photos.
Inside each pixel, there are color filters. These filters let the sensor detect colors like red, green, and blue. The camera mixes these colors to create the full range of colors in your photo.
Types Of Image Sensors
Two common types of image sensors exist: CCD and CMOS. Both capture light but work differently. CCD sensors are known for high-quality images. CMOS sensors use less power and cost less.
Most modern cameras use CMOS sensors. They offer fast processing and good image quality. Each sensor type suits different camera needs and budgets.
Image Processing
Image processing is a vital part of how a digital camera works. It turns raw data from the sensor into clear, colorful pictures. This process happens inside the camera’s processor in just seconds. Each step improves the quality of the photo. It also makes the file ready to save or share.
Signal Conversion And Noise Reduction
The camera sensor captures light as electrical signals. These signals are very weak and must change into digital data. This step is called signal conversion. The camera’s processor cleans up the data by reducing noise. Noise looks like tiny dots or grain in the photo. Removing noise makes images sharper and smoother, especially in low light.
Color Processing
The digital sensor sees light differently from human eyes. The camera uses color filters to capture red, green, and blue light. It then combines these colors to create a full-color image. The processor adjusts colors for balance and natural look. This step ensures the photo looks like the real scene.
Compression And Storage
Photos can be very large files. Compression shrinks the file size without losing much detail. This saves space on the memory card. The camera stores the compressed image in formats like JPEG or RAW. JPEG files are smaller and ready to use. RAW files keep more data for editing later.
Display And Review
The display and review features of a digital camera help photographers see their shots instantly. These tools allow quick checks and adjustments. They make the photo-taking process smoother and more enjoyable.
Lcd Screen Function
The LCD screen shows what the camera sees before a photo is taken. It helps frame the shot and check focus. The screen also shows menus and settings for easy control. Brightness can be adjusted for clear viewing in sunlight.
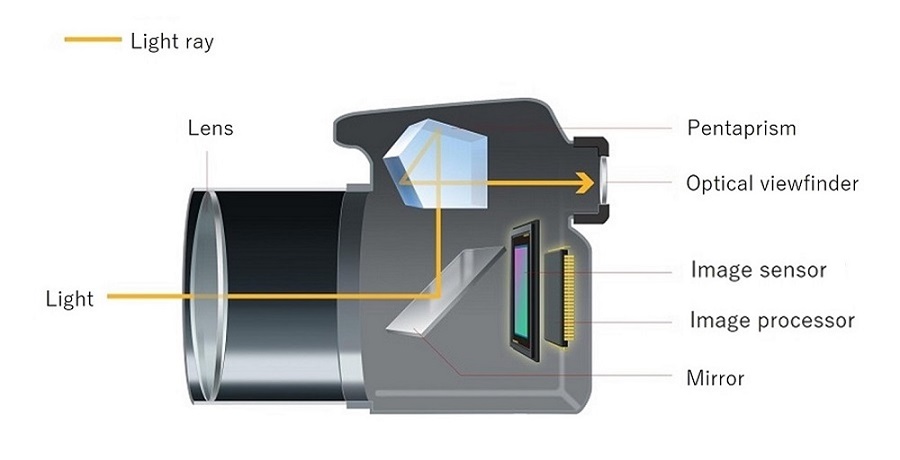
Viewfinder Options
Some cameras have an optical viewfinder to look through. It shows the scene directly through the lens or a separate window. Electronic viewfinders display a digital preview inside the camera. Both help to compose images better in bright light.
Image Playback
After capturing, the camera shows the photo on the screen. Users can zoom in to check details or delete unwanted shots. This feature allows quick review and saves time. It helps make sure the best photos are kept.
Advanced Features
Digital cameras have grown beyond simple picture-taking devices. Advanced features make capturing great photos easier and more fun. These tools help photographers get sharp, clear, and well-lit images in many situations. Let’s explore some key advanced features that improve camera performance.
Autofocus Systems
Autofocus helps the camera focus quickly and accurately. It locks onto the subject so the photo is sharp. Modern cameras use multiple focus points across the frame. This helps track moving subjects and focus on small details. Some cameras offer face or eye detection. This keeps people’s faces sharp in portraits. Autofocus saves time and reduces blurry photos.
Image Stabilization
Image stabilization reduces blur caused by camera shake. This is useful when holding the camera by hand. It allows slower shutter speeds without losing sharpness. Some cameras use sensor-shift technology to steady the image. Others use lens-based stabilization that moves parts inside the lens. Stabilization helps in low light or when zooming in. It makes photos clearer and videos smoother.
Hdr And Low Light Modes
HDR mode combines multiple shots to balance light and dark areas. It creates photos with more detail and better contrast. This is great for scenes with bright skies and shadows. Low light mode improves photos taken in dark places. It brightens images without adding too much noise. These modes help capture scenes as the eye sees them. They make photos look natural and vibrant.
Digital Vs Film Cameras
Digital and film cameras capture images differently. Each type has unique features that affect how photos look and how cameras operate. Understanding these differences helps photographers choose the right tool for their needs.
Differences In Image Capture
Film cameras use light-sensitive chemicals on a film strip to record images. The film must be developed in a darkroom or lab to see the pictures. Digital cameras use electronic sensors to capture light and turn it into digital data instantly. This allows photos to be viewed immediately on a screen.
Advantages Of Digital
Digital cameras offer many benefits. Photos can be edited easily on a computer. You can take many pictures without worrying about running out of film. Digital files are easy to store and share online. These cameras also allow quick adjustments to settings for different lighting and scenes.
Future Of Photography
Digital technology continues to improve camera quality and features. Smartphones now include powerful digital cameras, making photography more accessible. Film photography still has a special place for art and nostalgia. The future blends digital convenience with creative choices from both methods.
Credit: howthingswork.org
Credit: everpresent.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does A Digital Camera Capture Images?
A digital camera captures images by converting light into electronic signals. The lens focuses light onto a sensor. The sensor records the image as digital data. This data is processed and stored as a photo file on memory.
What Is The Role Of The Image Sensor?
The image sensor detects light and converts it into electrical signals. It replaces film in digital cameras. Common types include CCD and CMOS sensors. Sensor quality impacts image resolution and clarity.
How Do Lenses Affect Digital Camera Photos?
Lenses focus light onto the image sensor. They control sharpness, depth, and field of view. Different lenses suit various photography styles. Quality lenses enhance image detail and reduce distortion.
Why Is Image Processing Important In Digital Cameras?
Image processing improves photo quality by adjusting colors, brightness, and sharpness. It reduces noise and corrects lens flaws. Processing happens instantly before saving the image file.
Conclusion
Digital cameras capture moments by turning light into images. They use lenses to focus light onto sensors. Sensors then change light into digital data. This data creates photos you can see and share. Understanding how cameras work helps you take better pictures.
It also makes using your camera easier and more fun. Keep practicing, and your photos will improve with time. Enjoy capturing memories with your digital camera every day.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

