Have you ever wondered how your phone charges without plugging it in? Wireless chargers might seem like magic, but there’s a smart science behind them.
Understanding how wireless chargers work can help you make the most of this handy technology and keep your devices powered up with ease. Stick around, and you’ll discover the simple secrets that make wireless charging possible—and why it could change the way you charge your gadgets forever.
Basics Of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging lets you power devices without plugging cables. It uses energy transfer through air. This method is safe and simple. Just place your device on a charging pad. The device starts to charge automatically.
This technology is common in smartphones, earbuds, and smartwatches. It reduces wear on charging ports. Wireless charging is also very convenient for daily use.
Electromagnetic Induction
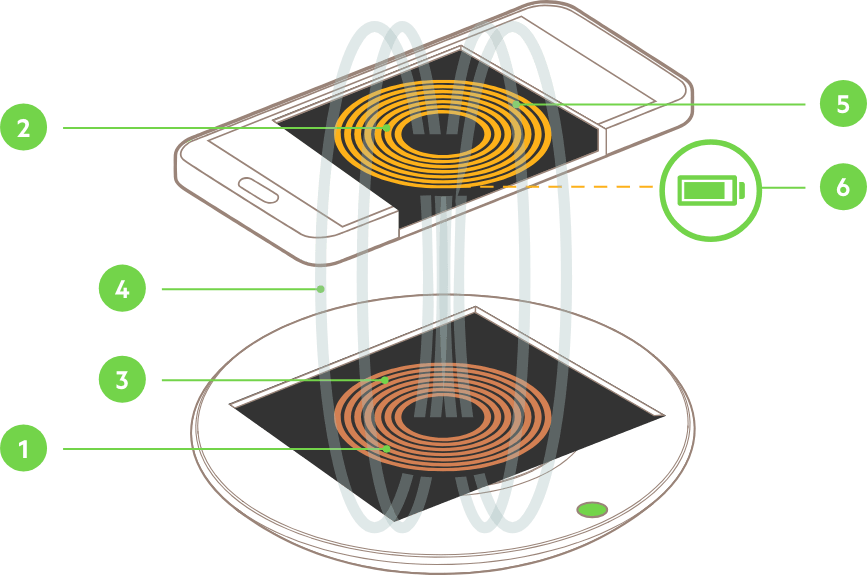
Electromagnetic induction is the core of wireless charging. It creates a magnetic field to transfer energy. A coil in the charging pad sends an alternating current. This current creates a magnetic field around the coil.
The device has a receiving coil. It captures the magnetic field and converts it back to electric current. This current then charges the battery. The process happens quickly and without wires.
Role Of Charging Pads And Receivers
Charging pads are the power source in wireless charging. They contain coils that generate magnetic fields. The pad connects to electricity through a cable or adapter. You place your device on the pad to start charging.
The receiver is inside the device. It has a coil that catches the magnetic energy. The receiver changes this energy into electric power. It sends power to the battery to keep the device running.
Both the charging pad and receiver must match in frequency. This match ensures efficient energy transfer. That is why some devices need specific chargers.
Credit: www.belkin.com
Types Of Wireless Charging Technologies
Wireless charging uses different technologies to transfer power without cables. These types vary in how they send and receive energy. Understanding these types helps to know how your device charges wirelessly.
Inductive Charging
Inductive charging works by creating a magnetic field between two coils. One coil is in the charger, the other inside the device. When aligned, the charger sends energy through the magnetic field. This energy then converts into electricity to charge the battery. This method is common in smartphones and small gadgets.
Resonant Charging
Resonant charging also uses magnetic fields but over a longer distance. The charger and device coils resonate at the same frequency. This resonance allows energy transfer even if the device is not perfectly aligned. It offers more flexibility than inductive charging. This method suits larger devices and some electric vehicles.
Radio Frequency Charging
Radio frequency charging sends power through radio waves. A transmitter sends waves that the device’s receiver converts into electricity. This method can charge devices at a distance without direct contact. It works well for small electronics like wearables and sensors. The technology is still developing for wider use.
Key Components In Wireless Chargers
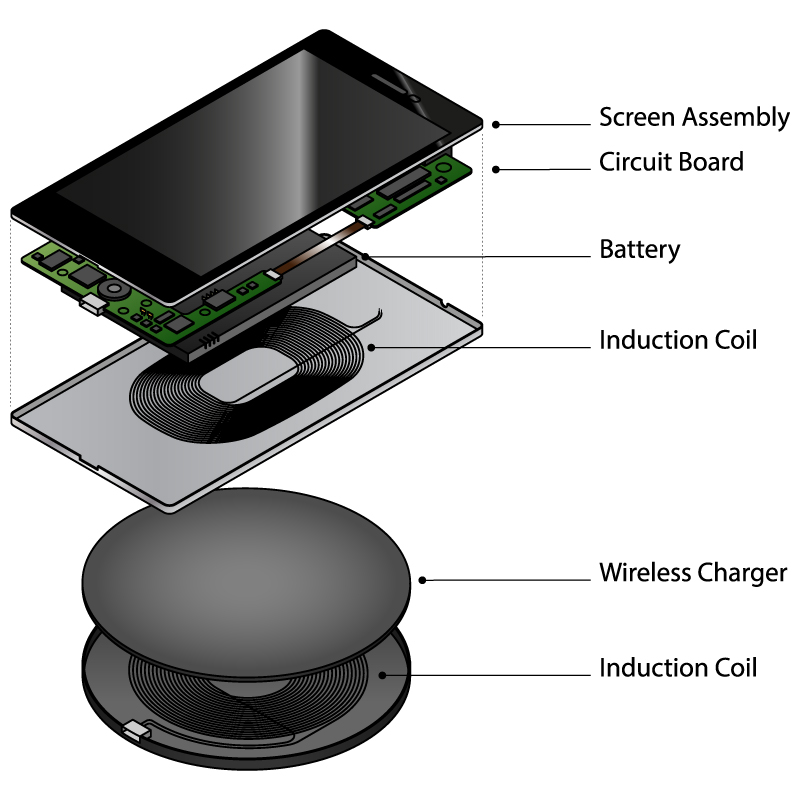
Wireless chargers use several important parts to send power without wires. These parts work together to move energy from the charger to your device. Understanding these parts helps explain how wireless charging works.
Transmitter Coil
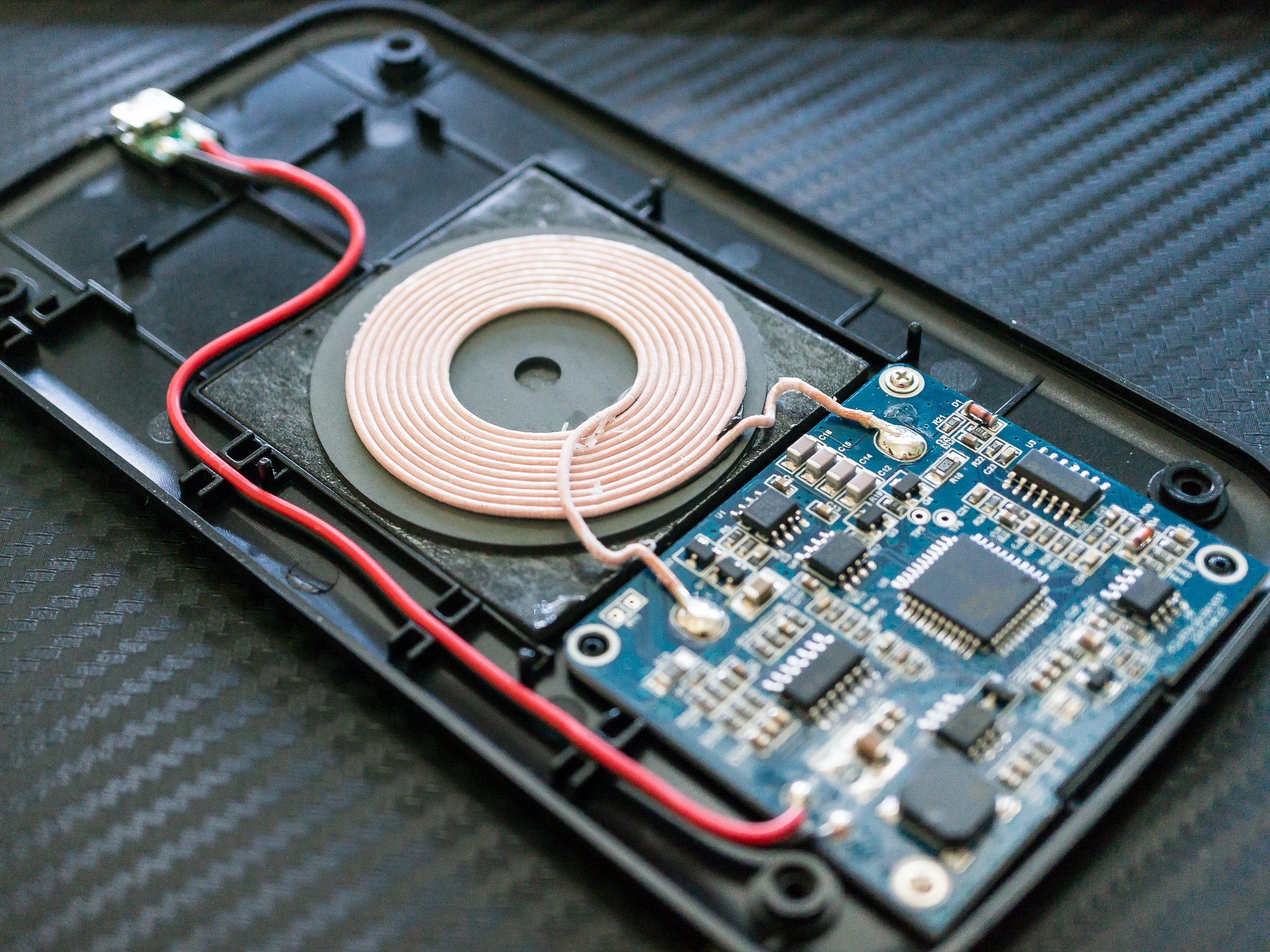
The transmitter coil is inside the wireless charging pad. It creates a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. This magnetic field carries energy to the device that needs charging. The coil’s shape and size affect how well it sends power.
Receiver Coil
The receiver coil is built into the device being charged. It catches the magnetic energy from the transmitter coil. Then, it changes that energy back into electricity. This electricity charges the device’s battery. The receiver coil must be close to the transmitter coil for good charging.
Power Management Circuitry
Power management circuitry controls the flow of electricity in both coils. It makes sure the charger sends the right amount of power. This protects the device from charging too fast or overheating. The circuitry also helps keep charging stable and safe.
Credit: www.nextgen-itsolution.com
How Energy Transfers Wirelessly
Wireless chargers work by sending power through the air. This process uses a special kind of energy transfer. It moves electricity without any wires or plugs. Understanding this helps explain how your devices charge simply by placing them on a pad.
The key to this system is the transfer of energy via magnetic fields. This method is safe and efficient. It allows chargers to power devices without direct electrical contact.
Magnetic Field Generation
Wireless chargers create a magnetic field using a coil of wire. When electric current passes through this coil, it produces a magnetic field. This field carries energy through the air. The charger’s coil acts like a tiny magnet. It sends out invisible magnetic waves that carry power.
Energy Conversion Process
The device to be charged has a receiver coil. This coil catches the magnetic waves from the charger. It changes the magnetic energy back into electrical energy. This electricity then charges the device’s battery. The whole process happens quickly and without wires.
Factors Affecting Charging Efficiency
Wireless charging is simple, but several factors affect its speed and efficiency. Knowing these can help you get the best charge for your device. Small changes in setup can make a big difference.
Distance And Alignment
Wireless chargers work by transferring energy through magnetic fields. The distance between the charger and your device matters. If the device is too far, charging slows down or stops. Proper alignment is also key. The charging coils in the device and charger must line up. Misalignment reduces power flow and wastes energy.
Material Interference
Materials between the charger and device can block energy transfer. Thick cases or metal objects cause interference. Some phone cases are too thick for wireless charging. Metal objects can heat up and disrupt the process. Removing cases or foreign objects improves charging speed and safety.
Device Compatibility
Not all devices use the same wireless charging standards. Devices and chargers must support the same technology, like Qi. Older devices may charge slower on new chargers. Using a charger designed for your device ensures faster and safer charging. Check your device’s specifications before buying a charger.
Safety Features In Wireless Charging
Wireless chargers have safety features to protect your device and the charger itself. These features stop damage from heat, objects, and other risks. They keep charging safe and efficient. Understanding these features helps you trust wireless charging technology.
Overheat Protection
Wireless chargers monitor temperature during use. If they get too hot, charging slows or stops. This prevents damage to your phone and charger. Overheat protection keeps both cool and safe. It also helps the charger last longer.
Foreign Object Detection
Chargers detect metal or other objects between the phone and charger. If an object is present, charging pauses. This avoids sparks or damage from metal objects. Foreign object detection protects your device and charger from harm. It ensures only your phone receives power.
Future Trends In Wireless Charging
Wireless charging is evolving fast. New trends aim to make it faster, easier, and more useful. These changes will impact how we charge our devices every day. Let’s explore some key future trends shaping wireless charging technology.
Faster Charging Speeds
Charging speed is a top priority for users. Future wireless chargers will deliver power much quicker. Advances in coil design and power management help reduce charging time. Faster wireless charging means less wait and more use time.
Long-distance Power Transfer
Current wireless charging needs close contact. Soon, devices may charge from a distance. This uses magnetic resonance or radio waves to send power over several feet. Imagine charging your phone without placing it on a pad.
Integration With Smart Devices
Wireless chargers will connect with smart home systems. They will work with voice assistants and apps for better control. Smart chargers can adjust power based on device needs. This makes charging safer and more efficient.
Credit: www.epectec.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Wireless Chargers Transfer Power?
Wireless chargers use electromagnetic induction to transfer power. A coil in the charger creates a magnetic field. This field induces a current in the phone’s coil, charging the battery without cables.
Are Wireless Chargers Safe For All Devices?
Yes, wireless chargers are generally safe for compatible devices. They regulate power to prevent overheating and damage. Always use chargers that meet safety standards and match your device specifications.
Why Is Charging Slower With Wireless Chargers?
Wireless charging is slower due to energy loss in magnetic induction. The process generates heat, reducing efficiency. Wired charging delivers power directly, making it faster than wireless methods.
Can Wireless Chargers Damage My Phone Battery?
No, wireless chargers do not damage phone batteries. Modern chargers control power flow to protect battery health. Using certified chargers helps maintain long-term battery performance.
Conclusion
Wireless chargers use magnetic fields to send power without cables. Devices just need to touch the charging pad. This method makes charging simple and neat. It works well for many smartphones and gadgets. Knowing how wireless charging works helps you use it better.
As technology grows, wireless charging will become more common. It saves time and reduces wire clutter. A small step toward easier daily tech use. Wireless charging is practical and user-friendly. Give it a try to enjoy cable-free power.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
