Are you confused about how to calculate AMT tax? You’re not alone.
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) can feel tricky, but understanding it is key to managing your taxes better and avoiding surprises. You’ll discover simple steps to figure out your AMT tax without getting lost in complicated formulas. By the end, you’ll feel confident about your tax calculations and ready to keep more of your hard-earned money.
Let’s break it down together.
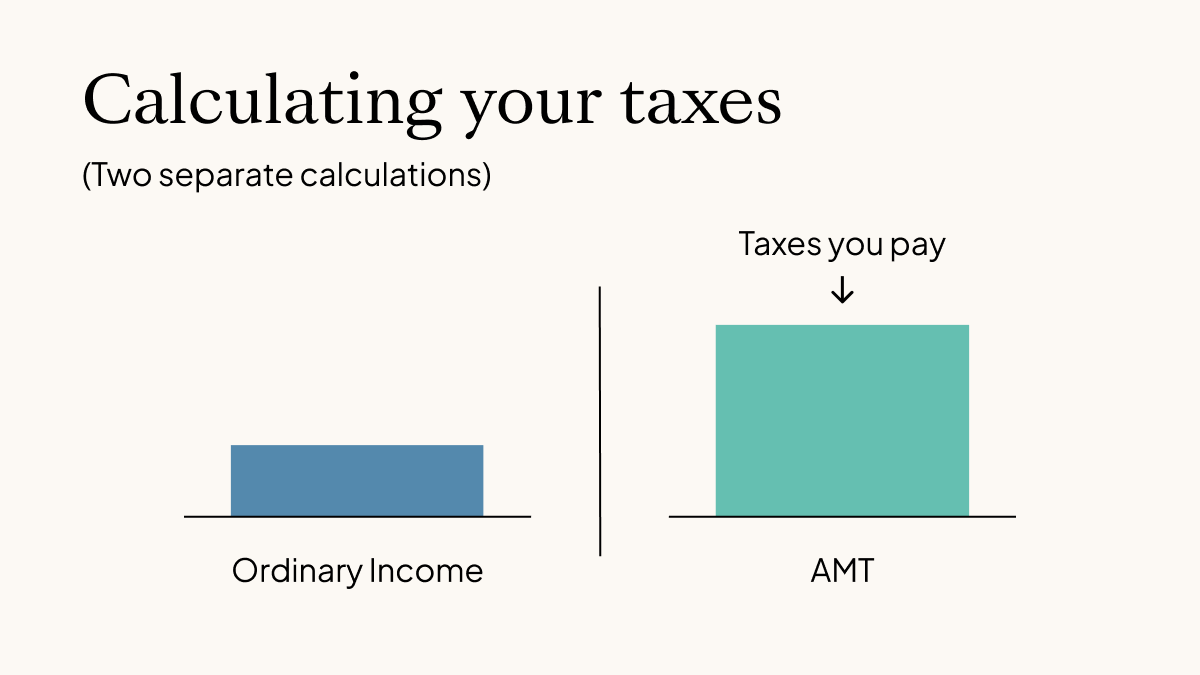
Credit: carta.com
What Is Amt Tax
Alternative Minimum Tax, or AMT, is a special tax system in the United States. It ensures that taxpayers pay at least a minimum amount of tax. This system prevents people from using too many deductions to lower their tax bill too much.
AMT runs alongside the regular income tax. You calculate both and pay the higher amount. It mainly affects those with higher incomes or many deductions.
How Amt Differs From Regular Tax
Regular tax uses standard rules and deductions. AMT removes some deductions and adds back others. This creates a different taxable income amount. The AMT rate is usually flat and can be higher than regular tax rates.
Who Must Pay Amt
Not everyone pays AMT. People with high incomes or many tax breaks face AMT more often. Examples include those with large state tax deductions or many dependents. AMT makes sure these taxpayers contribute a fair share.
Why Amt Exists
The government created AMT to stop very low tax payments. It closes loopholes in the tax code. AMT makes the tax system fairer by limiting excessive deductions.
Who Needs To Pay Amt
Understanding who must pay the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) is essential for many taxpayers. AMT aims to ensure that people with higher incomes pay a minimum level of tax. It applies differently than regular income tax. Knowing who faces AMT can help avoid surprises during tax season.
High-income Earners
People with high incomes often face AMT. The tax targets those with large earnings and many deductions. It limits the benefits of some tax breaks. This group usually includes professionals, business owners, and investors.
Taxpayers With Many Deductions
Those who claim many deductions may owe AMT. Common deductions like state and local taxes can trigger AMT. This tax reduces or removes these deductions. It ensures taxpayers still pay some tax despite deductions.
Individuals Exercising Stock Options
Employees using incentive stock options (ISOs) might pay AMT. The difference between the stock’s market price and option price counts as income for AMT. This can increase taxable income significantly. Many tech and startup workers face this issue.
Families With Large Exemptions
Families claiming large personal exemptions may owe AMT. AMT removes or reduces these exemptions. This leads to a higher taxable income for AMT purposes. Large families or those with dependents should be aware.
People With Capital Gains
Capital gains can increase the chance of AMT. When selling investments at a profit, gains add to income. This can push income above the AMT threshold. Taxpayers with big investment gains should check for AMT.
Key Components Of Amt Calculation
Calculating the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) requires knowing a few key parts. These parts help figure out how much tax you owe under the AMT rules. Understanding them makes the calculation clearer and easier.
Each part plays a special role in the process. They work together to set your final AMT amount. Below are the main components you must know.
Alternative Minimum Taxable Income
Alternative Minimum Taxable Income (AMTI) is your starting point. It begins with your regular taxable income. Then, certain tax benefits and deductions get added back. These include state tax deductions and some personal exemptions. The AMTI is often higher than regular taxable income. This helps ensure a minimum level of tax is paid.
Exemption Amounts
The exemption amount lowers your AMTI. It is a fixed dollar amount set by tax rules. This amount changes based on your filing status. Higher incomes may see the exemption reduced or removed. The exemption helps protect lower earners from paying AMT. After subtracting it, you get the income to tax under AMT rules.
Amt Tax Rates
AMT uses two tax rates: 26% and 28%. These rates apply to your income after exemptions. The 26% rate applies to income up to a certain limit. Income above that limit is taxed at 28%. These rates are different from regular tax rates. They make sure higher income pays a fair AMT share.

Credit: williamskeepers.com
Step-by-step Amt Calculation
Calculating the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) can seem tricky. Breaking it down into simple steps helps you understand it better. Follow these steps to find out your AMT liability clearly.
Calculate Regular Taxable Income
Start with your regular taxable income from your tax return. This is the income after all standard deductions and credits. It forms the base for your AMT calculation.
Adjust Income For Amt Preferences
Add back certain income and deductions not allowed under AMT rules. Examples include state tax deductions and some miscellaneous expenses. This adjustment increases your income for AMT purposes.
Subtract Exemption Amount
Next, subtract the AMT exemption amount based on your filing status. This exemption reduces your adjusted income. Note the exemption phases out at higher income levels.
Apply Amt Tax Rates
Apply AMT tax rates of 26% or 28% to your taxable income. Use 26% for most income and 28% for amounts above a set threshold. This gives your tentative minimum tax.
Compare With Regular Tax
Compare your tentative minimum tax to your regular tax. If AMT is higher, pay the difference as AMT. This ensures you pay at least the minimum tax required.
Common Amt Triggers To Watch
Understanding common AMT triggers helps you manage your tax bill better. The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) can affect many taxpayers unexpectedly. Certain expenses and income types can raise your AMT liability. Recognizing these triggers allows you to plan your finances smartly and avoid surprises.
High State And Local Taxes
State and local tax payments are not deductible under AMT rules. This can increase your taxable income for AMT calculation. Taxpayers in states with high income or property taxes often face higher AMT. Carefully tracking these taxes helps estimate your AMT impact.
Large Miscellaneous Deductions
Some miscellaneous deductions do not reduce income for AMT. Examples include unreimbursed employee expenses and investment fees. Large deductions here can trigger AMT by lowering regular tax but not AMT income. Monitoring these expenses can prevent unexpected AMT charges.
Incentive Stock Options
Exercising incentive stock options (ISOs) can create AMT income. The difference between the option price and market price counts as AMT income. Selling shares too soon or holding them too long affects AMT results. Planning ISO exercises carefully helps control AMT exposure.

Credit: www.mystockoptions.com
Strategies To Reduce Amt Liability
Reducing your Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) liability requires smart planning. Small changes in income and deductions can lower your AMT bill significantly. Understanding these strategies helps you keep more of your money. Focus on timing, managing investments, and using tax credits.
Timing Income And Deductions
Shift income to a year with lower AMT exposure. Delay bonuses or extra payments until next year. Accelerate deductible expenses like medical bills or property taxes into the current year. This reduces your current year’s AMT taxable income. Timing matters a lot in controlling AMT.
Managing Investment Income
Interest from private activity bonds triggers AMT. Choose municipal bonds that do not affect AMT instead. Avoid large capital gains in a high AMT year. Spread out sales of investments over multiple years. Careful investment choices reduce AMT impact.
Utilizing Tax Credits
Some tax credits reduce AMT directly. The foreign tax credit and the adoption credit often help. Use credits that apply to both regular tax and AMT. Keep track of which credits lower your AMT. Applying the right credits cuts your total tax owed.
Tools And Resources For Amt
Calculating Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) can be tricky. Many taxpayers find it hard to understand the rules and numbers. Using the right tools and resources makes the process easier and less stressful. These tools help to check if AMT applies and to calculate the correct amount.
Tax Software Options
Tax software can simplify AMT calculations. Most popular programs include AMT in their tax forms. They guide users step-by-step through the process. These tools automatically check for AMT and do the math. They save time and reduce errors. Some software even explains complex AMT rules in simple terms.
Professional Tax Help
Tax professionals have deep knowledge of AMT rules. They can review your financial details and spot AMT triggers. Experts ensure you pay the correct AMT amount. They also help plan your taxes to lower AMT in future years. Hiring a professional can bring peace of mind and accuracy.
Irs Amt Forms
The IRS provides specific forms for AMT calculations. Form 6251 is the main form used to figure AMT. It lists income adjustments and preferences that affect AMT. IRS instructions help taxpayers fill this form correctly. Accessing these official forms is important for accurate tax filing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Amt Tax And Why Is It Important?
AMT stands for Alternative Minimum Tax. It ensures taxpayers pay a minimum tax by limiting deductions. AMT prevents excessive tax avoidance. Calculating AMT is crucial for high-income earners to avoid surprises during tax filing.
How Do You Calculate Amt Tax Step-by-step?
Start with your regular taxable income. Add back specific tax preference items to find AMTI. Subtract the AMT exemption amount. Apply the AMT tax rates (26% or 28%). The result is your AMT liability if it exceeds regular tax.
Who Needs To Pay The Amt Tax?
Taxpayers with high income or large deductions often owe AMT. It targets individuals benefiting from certain credits or exclusions. If your AMT exceeds regular tax, you must pay the higher amount. Use tax software or professionals to check your AMT status.
What Deductions Are Disallowed In Amt Calculation?
Certain deductions like state and local taxes, and personal exemptions are disallowed. Miscellaneous itemized deductions are also excluded. This reduces your deductions, increasing your AMTI. Understanding these disallowed deductions helps in accurate AMT tax computation.
Conclusion
Calculating AMT tax is simpler than it seems. Start by understanding your income and deductions. Then, follow the step-by-step process carefully. Keep records of all relevant financial details. This helps avoid mistakes and surprises later. Knowing how to calculate AMT helps you plan your taxes better.
It also ensures you pay the right amount. Stay informed and review your tax situation yearly. This way, you can handle AMT with confidence and ease.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

