Are you trying to understand how much difference there is between two groups in your data? Calculating Cohen’s d can give you a clear number that shows the size of that difference.
But what exactly is Cohen’s d, and how do you figure it out step by step? If you want a simple, straightforward way to measure the impact or effect in your study, this guide is for you. Keep reading, and you’ll learn how to calculate Cohen’s d easily, so you can make your results more meaningful and powerful.

Credit: www.youtube.com
What Is Cohen’s D
Cohen’s d measures the difference between two groups in a simple way. You calculate it by subtracting one group’s average from the other, then dividing by the standard deviation. This shows how big the difference really is.
Cohen’s d is a statistic used to measure the size of an effect. It shows how much two groups differ. This helps us understand if the difference is small, medium, or large.
Researchers use Cohen’s d to compare group means in experiments. It is common in psychology, education, and social sciences. The value helps explain the practical importance of results.
The Meaning Of Cohen’s D Values
Cohen’s d values tell us about the strength of the difference. A small effect is around 0.2. A medium effect is near 0.5. A large effect is 0.8 or above.
These numbers guide researchers in interpreting results. They show if a treatment or change has a real impact. Small values mean less noticeable differences.
Why Use Cohen’s D
Cohen’s d helps compare results across studies. It works even if different scales or units are used. This makes it easier to understand and share findings.
The measure also helps in planning research. It shows how many participants might be needed. Strong effects need fewer participants to detect differences.
When To Use Cohen’s D
Cohen’s d is a popular way to measure effect size. It helps compare the difference between two groups. Knowing when to use Cohen’s d ensures your results make sense. This section explains the best situations for using Cohen’s d.
Comparing Two Group Means
Use Cohen’s d when you want to see how different two groups are. For example, test scores from two classes or treatment effects. It shows how big the difference is, not just if it exists.
Small Or Large Sample Sizes
Cohen’s d works well for both small and large groups. It gives a clear idea about the difference size, even if samples vary in size. This makes it a flexible tool.
Independent Or Paired Samples
You can use Cohen’s d with independent groups or paired samples. Independent means separate groups, like two different schools. Paired means the same group tested twice, like before and after a lesson.
Beyond Statistical Significance
Statistical tests only tell if a difference exists. Cohen’s d shows how big that difference is. This helps understand if the change matters in real life.
Gathering Your Data
Gathering your data is the first step in calculating Cohen’s d. You need accurate and clear information from your samples. Good data helps you find the true effect size between two groups. This step sets the foundation for your entire analysis.
Collecting Sample Means
Start by finding the average score of each group. The sample mean shows the central point of your data. Add all numbers in a group and divide by the total number of items. This gives you the mean for that group. Do this for both groups you want to compare.
Calculating Standard Deviations
Next, measure how spread out the data is around the mean. This is called the standard deviation. Calculate it for each group separately. It tells you how much the scores vary. A small standard deviation means scores are close to the mean. A large one means scores are more spread out.
Determining Sample Sizes
Count the number of observations in each group. This is the sample size. Knowing the size helps weigh the data correctly. Larger samples give more reliable results. Make sure to record the size for both groups before proceeding.
Calculating The Pooled Standard Deviation
Calculating the pooled standard deviation combines two groups’ standard deviations into one value. It helps measure the overall spread of data before finding Cohen’s d. This step ensures a fair comparison between group means.
Understanding The Pooled Standard Deviation
The pooled standard deviation combines the standard deviations of two groups.
It helps compare the differences between groups more fairly.
This value is important when calculating Cohen’s d for effect size.
Formula For Pooled Standard Deviation
The formula includes the standard deviations and sample sizes of both groups.
It gives a weighted average, balancing the sizes of each group.
Use this formula:
s_p = √ [ ((n₁ – 1)s₁² + (n₂ – 1)s₂²) / (n₁ + n₂ – 2) ]
Step-by-step Calculation Process
First, find each group’s variance by squaring their standard deviations.
Next, multiply each variance by its group size minus one.
Add these results together for the numerator.
Then, add the sample sizes and subtract two for the denominator.
Divide the numerator by the denominator.
Finally, take the square root of this result to get the pooled standard deviation.
Step-by-step Calculation Of Cohen’s D
Calculating Cohen’s d helps measure the difference between two groups. This effect size shows how far apart the groups are in standard deviation units. The process uses simple math but gives powerful insights. Follow these clear steps to find Cohen’s d easily.
Subtracting The Means
Start by finding the mean of each group. The mean is the average score of the group. Subtract the mean of the second group from the first group’s mean. This gives the difference between the two groups.
Dividing By Pooled Standard Deviation
Next, calculate the pooled standard deviation. This combines the variability of both groups. Use the formula that weights each group’s variance by its sample size. Then, divide the mean difference by this pooled standard deviation.
Interpreting The Result
The result shows how many standard deviations the groups differ. A larger number means a bigger effect. Values around 0.2 show a small effect, 0.5 a medium effect, and 0.8 or higher a large effect. This helps understand the practical importance of the difference.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Examples Of Cohen’s D Calculation
Examples help to see how Cohen’s d is calculated in real situations. They show the steps clearly. You learn how to measure the effect size between two groups. Below are two simple examples that explain the process.
Simple Numeric Example
Imagine two groups with test scores. Group A has an average of 80, and Group B has an average of 70. The standard deviation for both groups is 10. To find Cohen’s d, subtract the means: 80 minus 70 equals 10. Then divide this difference by the standard deviation, 10. So, Cohen’s d equals 1. This means the groups differ by one standard deviation. A value of 1 shows a large effect size.
Using Software Tools
Software like SPSS, R, or Excel can calculate Cohen’s d fast. You enter the group data or summary statistics. The program runs the formula and gives the effect size. This method reduces errors and saves time. It is useful for large datasets or many comparisons. Some tools even create graphs to visualize results.
Interpreting Cohen’s D Values
Interpreting Cohen’s d values helps understand the size of an effect. It shows how much two groups differ in a study. The value tells if the difference is small, medium, or large. This helps in deciding the importance of the results.
Small, Medium, And Large Effects
Cohen’s d values follow a simple scale. A small effect is around 0.2. It means a slight difference between groups. A medium effect is near 0.5. This shows a noticeable difference. A large effect is 0.8 or higher. It means a big difference in the study.
Contextual Considerations
Numbers alone do not tell the whole story. Context changes how to view Cohen’s d. Small effects can matter in some fields. Large effects may be rare in others. Always think about the study area and goals. This helps give the right meaning to the values.
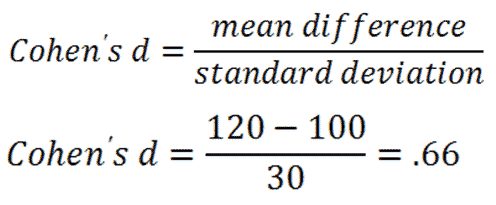
Credit: www.statisticslectures.com
Common Mistakes To Avoid
Calculating Cohen’s d can be tricky. Small errors can lead to wrong results. Avoiding common mistakes saves time and improves accuracy. This section highlights key errors to watch out for.
Using Incorrect Standard Deviation
Many confuse which standard deviation to use. Use the pooled standard deviation, not just one group’s SD. This ensures the effect size reflects both groups accurately. Using a single group’s SD can distort results.
Mixing Up Group Means
Swapping the two group means changes the sign of Cohen’s d. The absolute value shows size, but the sign shows direction. Be careful to subtract in the correct order to avoid confusion.
Ignoring Sample Size Differences
Sample sizes affect the pooled standard deviation. If groups differ in size, calculate weighted SD properly. Ignoring this leads to bias and inaccurate effect size estimates.
Not Checking Data For Outliers
Outliers can inflate standard deviation and distort Cohen’s d. Always examine data for extreme values before calculation. Removing or adjusting outliers improves reliability.
Confusing Cohen’s D With Other Effect Sizes
Cohen’s d is not the same as Pearson’s r or odds ratio. Each measures different concepts. Use the correct formula and interpretation for Cohen’s d only.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Cohen’s D In Statistics?
Cohen’s d measures the effect size between two groups. It shows the difference in means divided by the pooled standard deviation. This helps understand the practical significance of study results beyond p-values.
How Do You Calculate Cohen’s D Formula?
Calculate Cohen’s d by subtracting the two group means, then divide by their pooled standard deviation. The formula is: d = (M1 – M2) / SDpooled.
Why Is Cohen’s D Important In Research?
Cohen’s d quantifies effect size, showing how large or meaningful differences are. It aids in interpreting results and comparing study outcomes reliably.
What Values Indicate Small Or Large Cohen’s D?
A Cohen’s d of 0. 2 is small, 0. 5 is medium, and 0. 8 or higher is large. These benchmarks help assess the strength of effects.
Conclusion
Calculating Cohen’s d helps show the size of a difference clearly. It compares two groups by using their means and standard deviations. This measure gives a simple way to understand how big or small an effect is. Knowing how to calculate it supports better data analysis and clearer results.
Use Cohen’s d to explain findings in research or reports. Practice makes it easier to use correctly. Keep formulas handy and apply them step by step. This skill improves your ability to discuss study outcomes with confidence.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

