Understanding your luteal phase is key if you want to take control of your menstrual health or improve your chances of pregnancy. But how do you calculate the luteal phase accurately?
Knowing this simple step can help you predict ovulation, identify hormonal imbalances, and plan better for your cycle. You’ll discover easy methods to calculate your luteal phase and why it matters for your overall well-being. Keep reading to unlock the secrets your body is trying to tell you.
Luteal Phase Basics
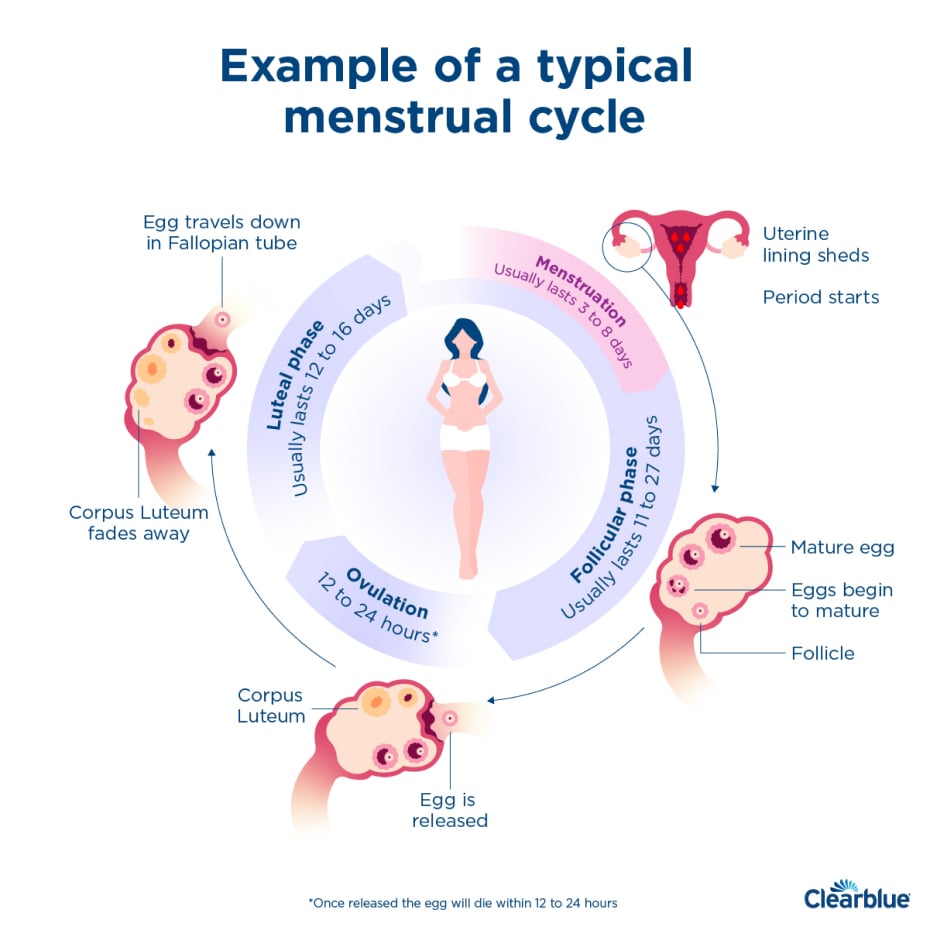
The luteal phase is a key part of the menstrual cycle. It happens after ovulation and before the period starts. Knowing the basics helps in understanding fertility and overall health. This phase affects hormone levels and the body’s readiness for pregnancy.
Understanding this phase can also help in tracking cycles more accurately. It provides insight into how the body works each month. Let’s explore what the luteal phase is and why it matters.
What Is The Luteal Phase
The luteal phase begins right after ovulation. It usually lasts about 12 to 14 days. During this time, the body produces a hormone called progesterone. This hormone prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg. If no pregnancy happens, progesterone levels drop. This drop triggers the start of the next period.
Importance In Menstrual Cycle
The luteal phase is important for fertility. It creates the right environment for a fertilized egg. A healthy luteal phase means the body supports pregnancy well. Short or irregular luteal phases can cause difficulties in conceiving. Tracking this phase helps in spotting cycle problems early. It also aids in planning pregnancy or understanding menstrual health.

Credit: conceiveplus.com
Tracking Your Cycle
Tracking your menstrual cycle helps you understand your body better. It is key to calculate the luteal phase accurately. The luteal phase is the time between ovulation and the start of your next period. By tracking your cycle, you can find the exact days to watch closely. This makes calculating easier and more precise.
Identifying Ovulation Day
Ovulation is when an egg leaves the ovary. This day starts the luteal phase. You can spot ovulation by watching your body’s signals. Some women feel slight pain or cramps. Others notice changes in cervical mucus; it becomes clear and stretchy. Another way is to use ovulation test kits. They detect hormone changes before ovulation.
Recording Menstrual Cycle Length
Write down the first day of your period each month. This is day one of your cycle. Count the days until the next period begins. Most cycles last between 21 and 35 days. Keep this record for several months. This helps find your average cycle length. Knowing this helps predict ovulation and luteal phase length better.
Calculating The Luteal Phase
Calculating the luteal phase helps understand the second half of the menstrual cycle. This phase starts after ovulation and ends just before the period begins. Knowing its length is important for tracking fertility and overall health.
Many women use this information to plan pregnancy or monitor cycle health. The luteal phase usually lasts between 10 and 16 days. Tracking it accurately can reveal important clues about hormonal balance.
Step-by-step Calculation Method
First, identify the day ovulation occurs. This is often day 14 in a 28-day cycle but can vary.
Next, count the days from ovulation until the day before the next period starts. This count is your luteal phase length.
Use a calendar or period tracking app to mark ovulation and period start dates. Count all the days in between carefully.
Repeat this process over several cycles to understand your average luteal phase length.
Common Formulas Used
One common formula is: Luteal Phase = Cycle Length – Ovulation Day. For example, a 28-day cycle with ovulation on day 14 gives a luteal phase of 14 days.
Another method uses basal body temperature (BBT) tracking. The luteal phase begins after a temperature rise and ends before the next period.
Some women also track hormone levels like progesterone to confirm the luteal phase.
These simple formulas and tracking methods help estimate the luteal phase easily.
Credit: www.clearblue.com
Tools For Accuracy
Calculating the luteal phase accurately helps understand your menstrual cycle better. Using the right tools can make this task easier and more precise. These tools track body signals and cycle patterns to give clear results.
Using Basal Body Temperature
Basal body temperature (BBT) is your body’s temperature at rest. Track it every morning before getting up. A small rise in BBT shows ovulation has happened. Counting days from this rise helps find the luteal phase length. Use a special BBT thermometer for better accuracy.
Ovulation Predictor Kits
Ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) detect hormone changes in urine. They indicate when ovulation is near. Testing daily around mid-cycle gives good results. Knowing the ovulation day helps calculate the luteal phase. OPKs are easy and quick to use at home.
Mobile Apps And Calendars
Mobile apps track periods and ovulation days. Enter your cycle data daily for best results. Apps predict luteal phase length based on your information. They send reminders to check temperature or use OPKs. Digital calendars make cycle tracking simple and organized.
Factors Affecting Luteal Phase Length
The length of the luteal phase can vary from person to person. Several factors influence how long this phase lasts. Understanding these factors helps in tracking fertility and menstrual health.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones play a key role in controlling the luteal phase. Progesterone is the main hormone that supports this phase. Low progesterone levels can shorten the luteal phase.
Other hormones like estrogen and luteinizing hormone (LH) also affect the timing. Imbalances in these hormones may cause irregular luteal phase length. Hormonal changes can result from stress, illness, or medical conditions.
Health And Lifestyle Impacts
Overall health and daily habits impact the luteal phase too. Poor nutrition or extreme weight changes can alter hormone levels. This may lead to a shorter or irregular luteal phase.
Stress affects hormone production and can disrupt the menstrual cycle. Lack of sleep and intense exercise also influence luteal phase length. Maintaining a balanced lifestyle supports a healthy luteal phase.

Credit: www.omnicalculator.com
When To Seek Medical Advice
Knowing when to seek medical advice about your luteal phase is important for your health. The luteal phase plays a key role in fertility and menstrual health. Some signs may show that this phase is not working well. Early action can help avoid bigger problems.
Signs Of Luteal Phase Defect
A luteal phase defect happens when the phase is too short or weak. Spotting these signs can help you act fast.
- Menstrual cycles shorter than 21 days
- Spotting before your period starts
- Difficulty getting pregnant
- Unusual cramps or pain after ovulation
- Low basal body temperature after ovulation
These signs suggest your body may not be producing enough progesterone. This hormone is needed to support pregnancy.
Consulting A Healthcare Provider
Visit a healthcare provider if you notice any signs of luteal phase defect. They can run simple tests like blood hormone levels or ultrasound scans. These tests check progesterone and the thickness of the uterine lining.
Early diagnosis helps your provider suggest treatments. These might include hormone therapy or lifestyle changes. Do not delay seeking advice if you have symptoms. Prompt care can improve your chances of a healthy cycle and pregnancy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Luteal Phase In A Menstrual Cycle?
The luteal phase is the post-ovulation stage of the menstrual cycle. It usually lasts 12 to 16 days and prepares the uterus for pregnancy.
How Do You Determine The Length Of Luteal Phase?
Subtract the ovulation day from the day your next period starts. The difference gives the luteal phase length.
Why Is Calculating Luteal Phase Important?
Knowing luteal phase length helps track fertility and identify potential hormonal imbalances or luteal phase defects impacting pregnancy chances.
Can Luteal Phase Length Vary Monthly?
Yes, luteal phase length can vary slightly but typically remains consistent. Significant changes may require medical consultation.
Conclusion
Calculating your luteal phase helps understand your menstrual cycle better. Count the days from ovulation to your next period. This number usually ranges between 10 and 16 days. Tracking it can reveal important health information. Knowing your luteal phase length aids in planning pregnancy or spotting issues.
Keep a simple calendar or use an app for accuracy. Regular tracking builds awareness of your body’s patterns. Small steps lead to better health knowledge. Stay consistent and patient for the best results.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

