As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Have you ever wondered how tiny computer chips are handled with such precision during manufacturing? Vacuum operated semiconductor wafer robots play a key role in this delicate process.
If you work in electronics or are simply curious about high-tech automation, understanding how these robots function can give you a fresh perspective on the invisible technology behind your devices. Keep reading, and you’ll discover how these smart machines use vacuum power to move fragile wafers safely and efficiently, making your gadgets possible.
Vacuum Robots In Semiconductor Industry
Vacuum robots play a key role in the semiconductor industry. They handle delicate wafers with care and precision. These robots use suction to pick up and move wafers safely. This method reduces the risk of damage during handling.
Vacuum robots work in cleanroom environments. They keep wafers free from contamination. Their design allows smooth and fast wafer transfer. This helps improve manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Role In Wafer Handling
Vacuum robots pick up semiconductor wafers using suction cups. These cups create a vacuum to hold the wafer firmly. This method avoids scratches and pressure marks on the wafer surface. Robots move wafers between machines and storage areas. They work quickly and accurately to meet production demands. Vacuum robots also reduce human contact with wafers. This lowers the chance of contamination and damage.
Advantages Over Mechanical Grippers
Vacuum robots cause less stress on wafers than mechanical grippers. Mechanical grippers use fingers or clamps that can damage wafers. Vacuum suction spreads force evenly across the wafer surface. This prevents cracks and breakage during handling. Vacuum robots also adapt better to different wafer sizes. They need fewer adjustments and less maintenance. Their design helps maintain cleanroom standards by reducing particle generation. Overall, vacuum robots offer safer and more reliable wafer handling.

Credit: www.researchgate.net
Key Components Of Vacuum Wafer Robots
Vacuum operated semiconductor wafer robots rely on several key components to move wafers safely and precisely. These parts work together to handle delicate wafers without damage. Understanding these components helps appreciate the robot’s role in semiconductor manufacturing.
Vacuum Suction System
The vacuum suction system holds the wafer during transport. It uses suction cups or pads that create a gentle vacuum. This vacuum grips the wafer firmly but without scratching it. The system adjusts suction power depending on wafer size and weight. It ensures wafers stay in place during movement.
Robot Arm And End Effector
The robot arm moves wafers between locations inside the machine. It is made from lightweight, strong materials for quick, smooth motion. The end effector is the part that touches the wafer. It often includes the vacuum suction system. Together, the arm and end effector handle wafers carefully and accurately.
Control Systems
Control systems guide the robot’s movements and operations. They use sensors and software to track wafer position and robot status. The system controls speed, direction, and suction power. It ensures precise handling to avoid wafer damage. These controls allow the robot to work efficiently in cleanroom conditions.
Working Principle Of Vacuum Operation
The working principle of vacuum operation in semiconductor wafer robots is simple yet effective. It uses suction to hold and move delicate wafers without damage. The vacuum creates a pressure difference, allowing the robot to pick up wafers securely. This method ensures precise handling and reduces the risk of contamination.
Creating And Maintaining Vacuum
The vacuum system starts with a pump or venturi device. This device lowers the air pressure inside the suction cup. The low pressure creates a strong grip on the wafer surface. To maintain the vacuum, seals and valves prevent air leaks. Consistent vacuum pressure is critical for steady wafer handling.
Wafer Pickup And Release Mechanism
The robot moves the suction cup to the wafer’s surface. The vacuum pulls the wafer up and holds it firmly. To release, the system stops the vacuum and lets air in. This gentle release avoids any damage to the wafer. The pickup and release process is quick and smooth.

Credit: siliconsemiconductor.net
Types Of Vacuum Grippers
Vacuum grippers play a key role in semiconductor wafer robots. They hold and move delicate wafers with care. Different types of vacuum grippers suit various wafer shapes and surfaces. Choosing the right gripper helps prevent damage and ensures smooth handling.
Here are the main types of vacuum grippers used in semiconductor wafer robots.
Flat Suction Cups
Flat suction cups have a smooth surface. They stick well to flat wafers. Their simple design offers strong suction. These cups work best with clean, flat surfaces. They provide stable grip without scratching the wafer.
Bellows Suction Cups
Bellows suction cups have a flexible, accordion shape. This shape helps grip uneven or curved wafers. They absorb shocks during handling. Bellows cups adapt to wafer surface changes. They reduce the risk of wafer damage.
Custom Designs For Wafer Shapes
Some wafers have unique shapes or sizes. Custom vacuum grippers fit these special wafers perfectly. They match the wafer contours exactly. Custom designs improve grip and safety. They make wafer handling more precise and reliable.
Automation And Precision Control
Automation and precision control are key in vacuum operated semiconductor wafer robots. These systems handle delicate wafers with high care. Automation reduces human error and speeds up the process. Precision control ensures wafers move exactly as needed. This keeps the manufacturing consistent and reliable.
Sensors And Feedback Loops
Sensors detect the wafer’s position and condition. They send data to the robot’s control system. Feedback loops use this data to adjust movements instantly. This helps maintain safe handling and prevents damage. Sensors also monitor vacuum pressure to secure the wafer properly.
Positioning Accuracy
The robot must place wafers with exact precision. It uses motors and actuators controlled by the system. Small errors can cause defects in semiconductor devices. Positioning accuracy ensures wafers align perfectly for processing. This accuracy is often within microns, very tiny distances.
Speed And Cycle Time Optimization
The robot balances speed with careful handling. Faster cycles increase production but risk wafer damage. Control systems optimize movements to reduce time without losing precision. This means wafers move quickly but safely through each step. Efficient cycle times improve overall manufacturing output.
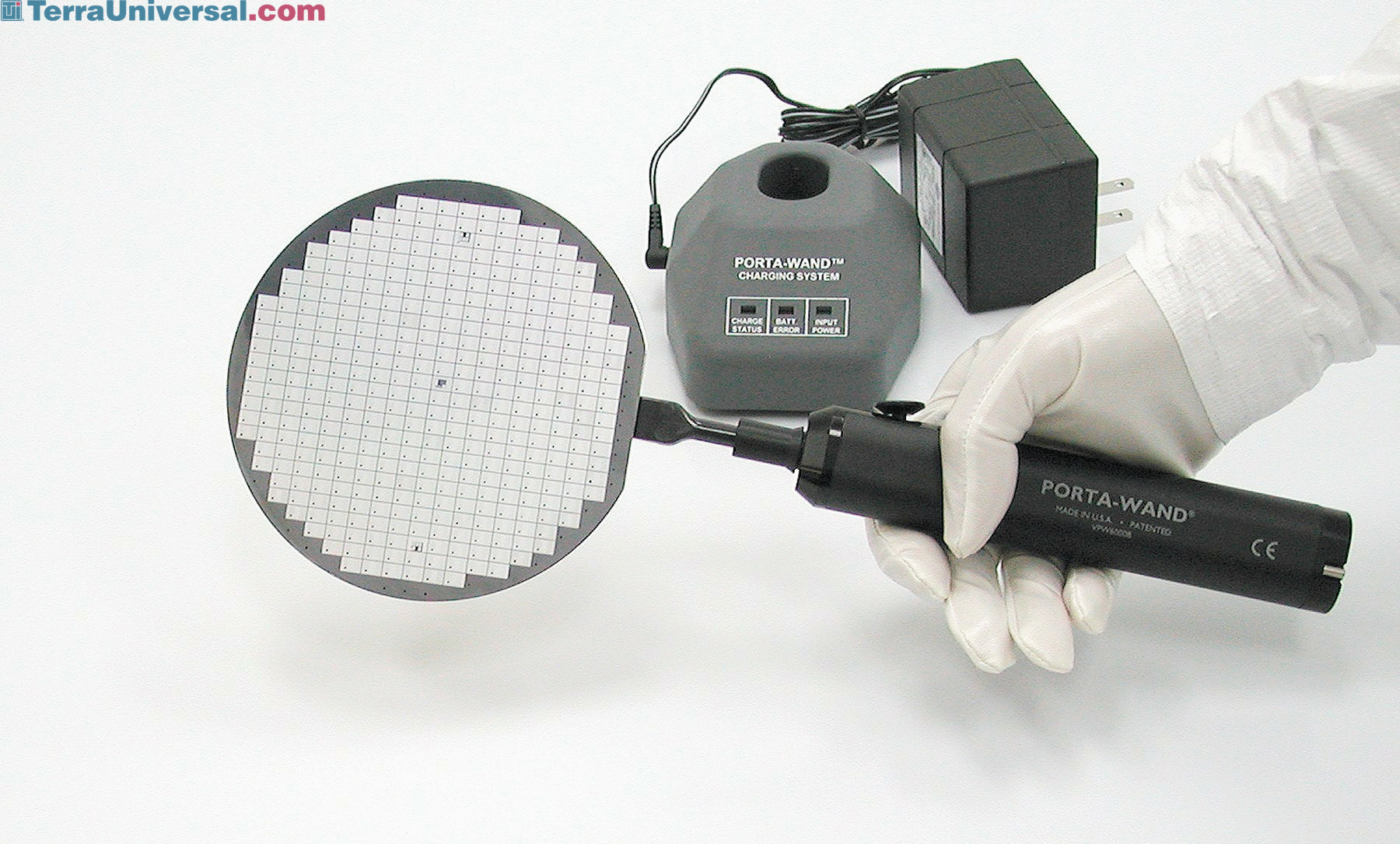
Credit: www.terrauniversal.com
Common Challenges And Solutions
Vacuum operated semiconductor wafer robots face several challenges during operation. These challenges affect performance and wafer safety. Understanding common problems helps improve reliability and efficiency. The following sections explain key challenges and practical solutions.
Maintaining Wafer Integrity
Wafers are thin and fragile. Handling without damage is critical. Robots use vacuum suction cups that hold wafers gently. Pressure must be balanced to avoid cracks or scratches. Soft materials on suction cups protect wafers. Regular inspection of the cups prevents wear and tear. Sensors monitor force during handling to ensure safety.
Vacuum Leak Prevention
Vacuum leaks reduce gripping strength and cause errors. Seals and hoses need regular checks to avoid leaks. Using high-quality vacuum components improves reliability. Detecting leaks early prevents wafer drops. Automated systems monitor vacuum levels continuously. Prompt maintenance fixes leaks before they affect operations.
Cleanroom Compatibility
Semiconductor manufacturing requires clean environments. Robots must not release particles or contaminants. Materials used are low outgassing and cleanroom rated. Designs minimize moving parts that produce dust. Regular cleaning keeps robots free from contaminants. Proper maintenance schedules ensure clean operation inside the cleanroom.
Future Trends In Vacuum Wafer Robotics
Vacuum wafer robots play a key role in semiconductor manufacturing. Their future looks promising with new technology trends. These trends aim to improve precision, speed, and efficiency. They also focus on reducing errors and costs. The development in this field will impact how wafers are handled and processed.
Integration With Ai And Machine Learning
AI helps robots learn from their actions. Machine learning allows robots to improve over time. This means better decision-making during wafer handling. Robots can detect and fix errors faster. They adapt to changes without human help. This makes the entire process more reliable and consistent.
Advanced Materials For Grippers
New materials make grippers lighter and stronger. These materials increase grip without damaging wafers. They resist wear and tear better than before. Some materials also work well in cleanroom conditions. This helps maintain wafer quality throughout the process.
Enhanced Automation Capabilities
Automation systems become more integrated and flexible. Robots can work with multiple machines at once. This reduces downtime and speeds up production. Sensors and controls improve to monitor tasks closely. Enhanced automation means fewer manual steps and errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does A Vacuum Operated Semiconductor Wafer Robot Function?
A vacuum operated wafer robot uses suction to grip and move delicate wafers. It creates a vacuum to securely hold wafers without damage. This allows precise handling and placement during semiconductor manufacturing processes.
What Components Make Up A Vacuum Wafer Robot?
Key components include the vacuum gripper, robotic arm, vacuum pump, and control system. The vacuum gripper holds wafers, the arm moves them, and the pump generates suction. The control system coordinates all movements for accuracy.
Why Use Vacuum Robots In Semiconductor Wafer Handling?
Vacuum robots reduce wafer damage by using non-contact suction handling. They improve precision and speed in wafer transfer, enhancing production efficiency. This method ensures contamination-free and safe wafer manipulation during delicate processes.
How Is Vacuum Pressure Controlled In Wafer Robots?
Vacuum pressure is regulated by sensors and valves within the robot system. These components maintain optimal suction strength to securely hold wafers. Proper control prevents wafer slips or damage during movement.
Conclusion
Vacuum operated semiconductor wafer robots move wafers precisely and safely. They use suction to hold wafers without damage. This method helps in clean and fast wafer handling. Robots improve efficiency in semiconductor manufacturing plants. Understanding their working helps appreciate modern technology better.
These robots play a key role in making electronics. Their simple yet effective design keeps production smooth. This technology continues to support the growth of the semiconductor industry.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.


