As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Have you ever wondered how websites remember your preferences or show ads that seem tailor-made for you? The secret lies in cookies and trackers.
These tiny pieces of data follow your online activity, shaping your browsing experience in ways you might not even notice. Understanding what cookies and trackers are can give you more control over your privacy and help you make smarter choices online.
Keep reading to uncover how they work and why they matter to you.
Cookies Basics
Cookies and trackers play a key role in how websites remember you. They help sites work better and offer a smoother experience. Understanding the basics of cookies is important for anyone using the internet.
This section explains what cookies are, the types of cookies, and how they work.
What Cookies Are
Cookies are small files stored on your device by websites. They hold information about your visit. This data helps websites recognize you when you return.
Cookies do not contain viruses or harm your device. They only store simple data like preferences or login status.
Types Of Cookies
There are two main types of cookies: session and persistent.
Session cookies last only while you browse a site. They disappear when you close the browser.
Persistent cookies stay on your device for a set time. They remember your preferences for future visits.
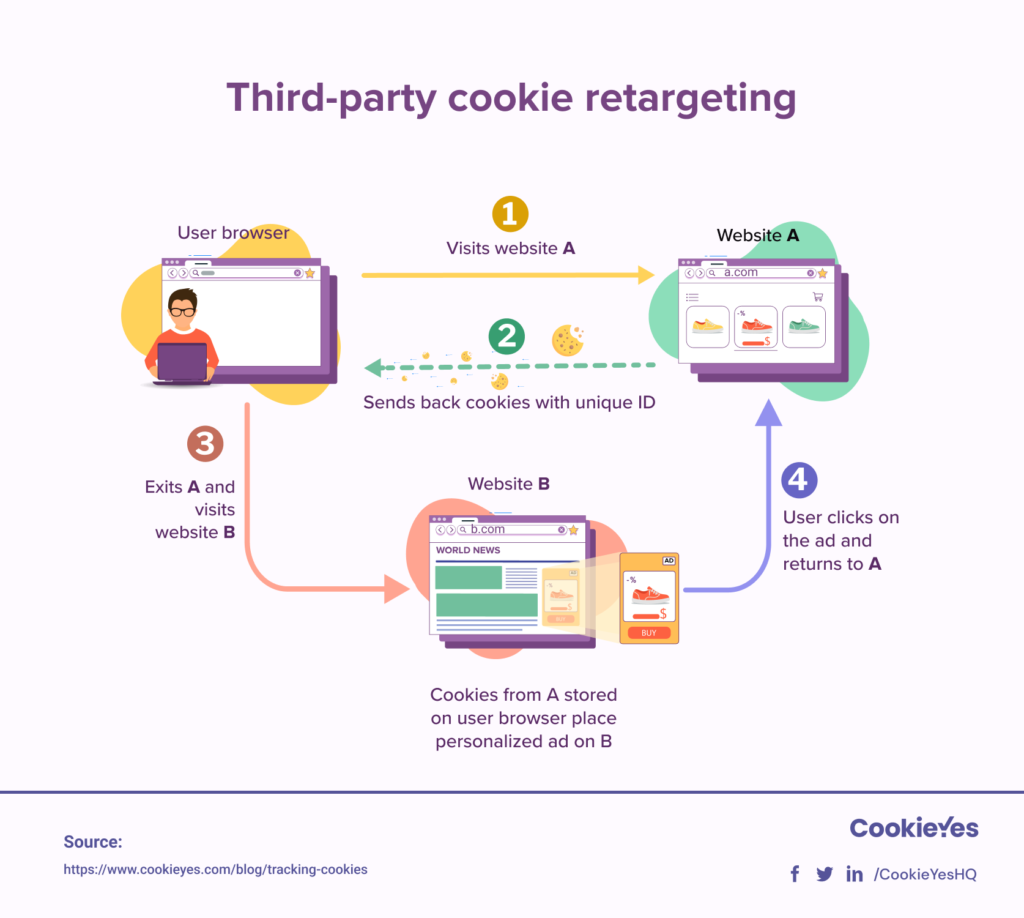
Other types include first-party and third-party cookies. First-party cookies come from the website you visit. Third-party cookies come from other sites, often for ads or tracking.
How Cookies Work
When you visit a website, it sends a cookie to your browser. Your browser saves this cookie on your device.
On your next visit, the browser sends the cookie back to the website. This lets the site recognize you and your preferences.
Cookies can store login details, language settings, or shopping cart items. They make browsing faster and easier.
Trackers Explained
Trackers are tools websites use to collect data about visitors. They help understand user behavior on the site. This information improves user experience and helps businesses target ads better.
Some trackers follow users across different websites. They build profiles to show relevant content or ads. Not all trackers are harmful, but privacy concerns exist.
What Trackers Do
Trackers collect data like pages visited, clicks, and time spent. They identify user preferences and interests. This data allows websites to customize content. Marketers use it to create targeted advertising campaigns.
Common Tracking Methods
Cookies are small files stored on your device. They save login details and preferences. Pixel tags are tiny images that load when you visit a page. They report your visit to the server. Browser fingerprinting collects information about your device and settings. This method can track you without cookies.
Differences Between Cookies And Trackers
Cookies store information on your device. Trackers include cookies and other tools. Not all trackers use cookies. Some track without saving files on your device. Cookies mostly help with site functionality. Trackers focus on user behavior and advertising.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy concerns have grown because of cookies and trackers. These tools collect data about users without clear permission. Many people worry about how their personal information is used and shared online.
Websites use cookies to store information about visitors. Trackers follow user behavior across multiple sites. This raises questions about consent and control over data.
How Cookies Affect Privacy
Cookies save details like login status and preferences. Some cookies track browsing habits across different sites. This can reveal a lot about a person’s interests and routines.
Not all cookies are harmful. But some collect data without clear notice. This can lead to unwanted sharing of personal information.
Tracking And User Profiling
Trackers gather data to create user profiles. These profiles help advertisers target specific audiences. This means users see ads based on their online actions.
Profiling can feel intrusive. It exposes private habits and preferences to companies. Users often do not know the full extent of tracking.
Risks Of Data Collection
Collected data can be hacked or leaked. This puts personal details at risk. Identity theft and fraud are possible dangers.
Data collection can also lead to discrimination. Companies might use profiles in unfair ways. Privacy laws try to limit these risks but are not always enough.

Credit: us.norton.com
Security Risks
Cookies and trackers help websites remember users and preferences. They also collect data about browsing habits. Despite their convenience, they pose security risks. These risks can expose personal information and lead to cyberattacks. Understanding these dangers is crucial for online safety.
Cookie Theft And Hijacking
Cookies store login details and session information. Cybercriminals can steal these cookies through attacks. This theft allows them to hijack user accounts. They can access sensitive data or act as the user. Such attacks put online privacy at serious risk.
Malicious Trackers
Some trackers are designed to harm users. Malicious trackers collect data without consent. They may install harmful software or redirect users to unsafe sites. These trackers can be hard to detect. They create vulnerabilities that hackers exploit easily.
Impact On Personal Data Security
Cookies and trackers collect a lot of personal data. This data includes browsing history, preferences, and location. If this information falls into the wrong hands, misuse can occur. Identity theft and fraud are common threats. Protecting personal data is vital to avoid these risks.
Managing Cookies And Trackers
Managing cookies and trackers is important for your online privacy. These small files collect data about your browsing habits. Controlling them helps protect your personal information. You can adjust settings or use special tools to limit tracking. This section explains how to manage cookies and trackers effectively.
Browser Settings And Controls
Most browsers let you control cookies and trackers. You can block third-party cookies or delete all cookies. Some browsers offer “Do Not Track” options. These settings reduce how much data websites collect. Checking your browser’s privacy settings is a good first step.
Using Privacy-focused Tools
Privacy tools add extra protection against trackers. Extensions like ad blockers stop many trackers automatically. Some browsers focus on privacy and block trackers by default. Using these tools lowers the risk of being tracked online. Choose tools that are easy to use and update regularly.
Best Practices For Users
Clear cookies regularly to remove stored trackers. Avoid clicking on suspicious links or ads. Use private browsing modes to limit cookie storage. Review app permissions on your devices often. These habits help keep your data safer while browsing.

Credit: www.termsfeed.com
Legal And Regulatory Aspects
Cookies and trackers collect data from website visitors. This data helps businesses improve their services and target ads. Legal rules now control how these tools can be used. These laws protect user privacy and personal information.
Privacy Laws Affecting Cookies
Many countries have laws about using cookies. The European Union’s GDPR is strict about data protection. It requires websites to get permission before using most cookies. The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) also limits how companies use personal data. These laws aim to give users control over their information.
Compliance Requirements
Websites must follow rules to use cookies legally. They need clear privacy policies explaining cookie use. Many sites show cookie banners asking for user consent. Businesses must keep records of consent and allow users to change preferences. Non-compliance can lead to fines and penalties.
User Rights And Consent
Users have rights to control their data. They can accept or reject cookies on websites. Laws require websites to get clear, informed consent. Users can also ask for their data to be deleted. This respects privacy and builds trust between users and websites.
Future Trends
The future of cookies and trackers is changing fast. New technology shapes how data is collected and used. Privacy concerns push for better rules and tools. Users will see many changes in tracking methods and protections.
Evolving Tracking Technologies
Tracking tools are getting smarter and less obvious. Companies use new methods like fingerprinting and server-side tracking. These do not rely only on cookies. They collect data in different ways to understand user habits.
Artificial intelligence helps analyze data better and faster. This means more personalized ads and content. Tracking will blend more into everyday browsing without interrupting users.
Improving Privacy Protections
Privacy laws are growing worldwide. Many countries require websites to get clear permission before tracking. Browsers block third-party cookies by default now. New privacy tools help users control what data they share.
Tech firms work on solutions like differential privacy. This hides individual data while still providing useful insights. Privacy will be a top priority in future tracking systems.
What Users Should Expect
Users will have more control over their online data. Clearer choices about tracking and data sharing will appear. Some tracking will continue but with better privacy safeguards.
Expect smoother web experiences with fewer interruptions. Transparency about data use will improve. Users can protect their privacy while still enjoying personalized content.
Credit: www.cookieyes.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Cookies In Web Browsing?
Cookies are small data files stored on your device by websites. They help websites remember your preferences and login status. Cookies improve user experience by personalizing content and saving browsing sessions securely.
How Do Trackers Collect My Online Data?
Trackers use scripts or pixels to monitor your web activity. They gather data like visited pages, clicks, and time spent. This information helps advertisers deliver targeted ads and analyze website performance effectively.
Are Cookies And Trackers Safe To Use?
Most cookies and trackers are safe and used for better user experience. However, some may collect excessive data without consent. Always review privacy settings and clear cookies regularly to protect your online privacy.
Can I Disable Cookies And Trackers On Websites?
Yes, you can disable cookies and trackers via browser settings or privacy tools. This limits data collection but may reduce website functionality or personalized features. Use selective blocking for a balanced browsing experience.
Conclusion
Cookies and trackers help websites remember your actions and preferences. They make browsing smoother and more personalized. But they also collect data about your habits online. Understanding how they work gives you more control over your privacy. You can manage or block cookies through your browser settings.
Staying aware helps keep your information safer. Remember, not all cookies are bad; some improve your web experience. Knowing the difference is key to browsing smart and safe.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
